Figure 3 Abaco 6U OpenVPX single-
board computer and a Rugged
System Enclosure
The Root of Trust
At the lowest level, a robust AT design
requires a root of trust, or a certified
CPU-based
hardware/firmware
element that provides the basis for
a secure boot process. The root of
trust validates the next stage, starting
a sequential process that builds
the trusted system as each stage
is validated. This protects against
executing untrusted code, detects
use of modified security values, and
prevents software attacks. Intel and
Freescale processors provide methods
to that end using cryptographic keys
and certified, un-modifiable BIOS
or bootROMs. These features are
discussed in the following sections.
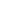
Another critical component is the
FPGA-based security hub - a central
system monitor that detects and
provides customized responses to
tamper events. The security hub
works with the trusted processing
system and provides independent
control to manage AT policies. Finally,
encrypted storage is used to protect
data and application software. An
example architecture is shown in
Figure 4.
COTS Trusted Execution
Intel Trusted Execution Technology
Intel Trusted Execution Technology
(TXT) defines a safe, isolated software
execution space that cannot be
observed or modified by unauthorized
software. The execution space
has dedicated resources that are
managed by the processor, chipset,
and operating system kernel. The
Figure 4 The FPGA Security Hub in an Intel-based Architecture
New-Tech Magazine Europe l 43