Technical article
November 2013
57
www.read-eurowire.comsoft and properly soldered ribbon has
to be used. Accurate laying of the PV
ribbon also has to be ensured during the
stringing, tabbing process. Good quality
interconnect ribbon will inevitably reduce
stringer downtime and its scrap rate.
Today’s high-speed stringers require ever
more demanding ribbon specifications.
The three key trends in PV ribbon
specifications include:
• Ever tighter tolerances of solder
thickness and ribbon straightness
are driven by new generation fully
automated, high-output stringers
• Lower ribbon yield strengths (Rp0.2%)
are required for increasingly thin solar
cells
• New panel designs utilise three
interconnect ribbons per cell instead
of two, reflected in a growing demand
for smaller (narrower and thicker)
ribbons. This in turn drives capacity
expansion of precision tinning lines for
small interconnect ribbons
PV ribbon
specifications and
requirements
The conductor or base material in the PV
ribbon is high-conductivity, high-purity
copper. Copper used in PV ribbons
is typically ETP, DIP form copper or
oxygen-free copper (OFC: CD-110, CD-101,
CD-102).
Copper wire is rolled in a rolling mill
to produce copper ribbons, which
are subsequently tinned/soldered in a
tinning line to produce PV ribbon. Some
producers use an alternative process of
copper strip slitting to produce copper
ribbons, which are generally of lower
quality.
The size range of bare copper ribbons
(inlet material for tinning line) is as follows:
• PV bus bar: width [3mm-6mm] x
thickness [0.2mm-0.5mm]
• Interconnect ribbon: width [1mm-3mm]
x thickness [0.08mm-0.2mm]
Copper ribbon tolerances vary among
producers. They depend mainly on the
type of rolling mills deployed, the quality
of input material and the know-how of
the manufacturer. Typical tolerances for
producers with good rolling capabilities
are:
• Width tolerance: ±8 micron-±15
micron
• Thickness tolerance: ±8 micron-±13
micron
The mechanical properties of PV ribbon
that are commonly sought by panel
manufacturers are:
• Tensile strength: <250 MPa
• Elongation: >20%
• Camber: <0.5% [5mm on 1m long
sample]
• Yield strength (Rp0.2%)
• Hard/semi hard >120 MPa
• Soft <80 MPa
• Super soft <65 MPa
PV ribbon straightness, also known
as camber, is measured in terms of
millimetres off a straight line on one metre
long ribbon sample.
Maximum level of camber is determined
by the stringing process and typically
ranges between <8mm/metre and <5mm/
metre.
There are different types of solder
compositions used in PV ribbon. They
depend on the stringing/soldering tech-
nique deployed by the panel manufacturer
and the local health and safety standards
related to panel manufacturing.
Common solder compositions are as
follows:
• Lead-free solder: Sn 100
• Lead containing solder: SnPb 60/40
• Silver containing solder: SnAg 96.5/3.5;
SnAgCu 96.5/3.0/0.5
• Lead and silver containing solder:
SnPbAg 62/36/2
• Low temperature solder: BiSn 57/43;
BiSnAg 57.7/42/0.3
Solder coat thickness ranges from 10
micron to 40 micron, with tolerances
between ±10% and ±30%. The most
common solder coat thickness is 20
micron ±4 micron.
There are three types of solder coat
thickness measurement technique:
• X-Ray: off-line measurement used for
one-side thickness measurement
• Manual micrometer: off-line measure-
ment used for measuring the total
thickness of two sides of the coat
• Laser: in-line measurement that can
be deployed on the tinning line and is
used for measuring the total thickness
of two sides of the coat during PV
ribbon production
PV ribbon is also inspected visually or with
a microscope to examine coating quality,
which should be without defects such as
stains, debris, burrs, dents, discoloration,
bare copper visible through solder
coating, small pinholes and other kinds of
mechanical defects.
Most of the above specifications and
corresponding measurement techniques
are defined in the standards for PV ribbon
that were introduced in August 2011. They
are available at
www.semi.organd include:
• SEMI PV18-0811: Guide for Specifying a
Photovoltaic Connector Ribbon
• SEMI PV19-0811: Guide for Testing
Photovoltaic
Connector
Ribbon
Characteristics
Finished PV ribbon products are packed on
spools/reels or discs/pancakes. The most
common spools used for PV ribbon in
Europe are DIN K125, K160, K200 and K250
and in Asia also P4 and P10.
Critical quality
parameters for
PV ribbon
All of the above PV ribbon specifications
are important in their own way. Type of
copper and its purity determines material
conductivity and the maximum level
of softness achievable for the ribbon.
Solder composition, its coat thickness and
coating composition influence the quality
of solder joint and panel durability.
High elongation of PV ribbon is important
to prevent failure of solder joints between
the bus bar and interconnect ribbon,
which may occur due to stretching/
tension due to temperature oscillations
during the panel operation. Continuous
daily, sometimes extreme temperature
fluctuations during the lifetime of the solar
▲
▲
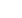
Figure 2
:
Solar panel with interconnect ribbons
soldered onto cells and bus bar around the panel
perimeter
▼
▼
Figure 3
:
Cross-section of a typical hot-dip tinned copper ribbon