61
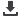
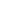
Figure 11:
The role of ecosystems in the global carbon cycle.
Ecosystem restoration can therefore play a role in mitigating cli-
mate change, mainly through increasing carbon sequestration
and storage. Forests, typically the most carbon-dense terrestrial
ecosystems, often receive most attention in climate policy.
It is especially relevant that the negotiations on reducing emis-
sions from deforestation and forest degradation (REDD) in de-
veloping countries under the UN Framework Convention on
Climate Change (UNFCCC) have expanded to include other
forest activities (“REDD+”). It is possible that new funds for
carbon-focused restoration, afforestation or reforestation ef-
forts could emerge (Miles, 2010).
Forest restoration usually involves either reforestation or man-
aging degraded forests with the aim of bringing them back
towards a ‘natural’ state. Restoration can be achieved either
through controlling pressures on forests, such as fires, inva-
sive species or unsustainable harvest, or through techniques to
speed forest recovery such as planting programmes or attract-
ing seed dispersers.
Other reforestation or afforestation approaches, such as com-
mercial tree plantations using non-native species or intensive
management techniques, fall short of ecosystem restoration
objectives but do also sequester carbon. These new forests are
less likely to provide other ecosystem services or biodiversity
benefits, and may be less resilient to the effects of climate
change on their carbon stores.
Sometimes forest restoration or afforestation is undertaken with
support from carbon finance in recognition of its role in cli-
mate change mitigation. For example, in the Scolel Te project in
Mexico, farmers planted over 700 ha of trees on degraded land
to sequester carbon, funded by the carbon offset market which
generated USD 180 000 in 2002 (Tipper, n.d.). Carbon credit
sales were also used to restore 36500 ha of Caribbean pine for-
est in Belize, creating a 0.013 GtC benefit over 55 years, as well
as protecting wildlife and enhancing soil quality (Walden, n.d.).
Carbon stored in soils forms a large part (~81%) of the total
terrestrial store (IPCC, 2001, 2007), but has been degraded
over wide areas. Depletion of soil organic carbon (SOC) may
Carbon cycle
- - --
-
- - -
--
-
-
150
918
38 100
650
50
Intermediate and Deep ocean
Dissolved organic C
Labile
dissolved
organic C
Sediments
Ocean surface
Marine
biota
3
11
6
6
0.2
39
50
101
RICCARDO PRAVETTONI - GRID-Arendal