TAR NC Implementation Document – Second Edition September 2017 |
63
Approaches other than allowed for capacity weighted
distance reference price methodology
Average pipeline distance
In general, pipeline distance is the distance along a defined pipeline. If two or more
pipelines with different lengths connect the same entry and exit point, then it is
possible to calculate alternative distances; one can determine both the shortest
distance and the average.
The calculation of average distance could require a large amount of data, since a
TSO’s networks often contains many entry and exit points. It can be useful to simplify
the representation of the network to simplify the calculation of average distances.
Airline distance
The airline distance is the result of computations that apply the Pythagorean
Theorem to coordinates assigned to each point. Airline distance is analogous to
using a ruler to measure the distance between two points on a flat map.
The logic of the calculation is: (a) to assign coordinates to each point: easting and
northing; and (b) to apply the following formula:
Where:
Distance
(En,Ex)
distance between the entry point and the exit point in km;
East
En
, East
Ex
easting of the entry or exit point according to the projected
coordinate system;
North
En
, North
Ex
northing of the entry or exit point according to the projected
coordinate system.
Assuming a flat surface implies an approximation only, whose accuracy may be
sufficient depending on terrain topography. Airline distance does not consider the
extra length of detours that uneven terrain may require, and does not consider
differences in altitude.
There are two ways to calculate airline distance:
\\
The Universal Transverse Mercator projected coordinate system (UTM), intro-
duced across Europe;
\\
Geo Information System (GIS), software normally available to TSOs, which
allows for the calculation of distance independent of the coordinate system
used.
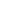
North
in km
Entry point:
North: 41 km
East: 30 km
Exit point:
North: 37 km
East: 33 km
East in km
Airline distance:
√ (41–37)
2
+ (30–33)
2
= 5
Figure 17:
Simple example of airline distance calculation