Noise
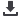
Theoretically, the number of photons that reach the detectors can be described as a
cascade of Bernoulli distribution, describing the probability that a photon is emitted or
not, absorbed from the patient or not, detected or not etc. This cascade can be
approximated with a Poisson distribution and hence we can write:
Meaning that the variance of the distribution is equivalent to the expected number of
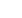
photons. This means that for a high number of photons also the noise is increasing, but
the SNR will overall decrease since
The noise is theoretically uncorrelated, but the cross-talk between adjacent detectors,
the logarithmic operation to obtain the sinogram, and especially the filtering of the
sinogram and backprojection operations make such that the noise is spatially correlated
in image domain.