Single Lab Validation Report for GOS in Infant Formula and Adult Nutritionals
20
12.4.
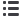
GOS is calculated as follows (g GOS/ 100 g reconstituted product):
(
)
(
)
used is
1.485
galactose;
from GOS
calculate
factor to
k
product
g 100 n to
calculatio
d
collection
fraction
e
preparativ
by
dilution
c
(mL)
flask
c
volumetri
volume
b
mg/mL n to
calculatio
a
:
legend
*
(mg)
product
ted
Reconstitu
100 *
25
1000 * 50*
1000
)
342
180 *(C-D) -B- (A
*
(g)
product
(g)
water
(g)
product
product
g 100 per
GOS
Amount
: es
concentrat
liquid and
powders
ted
Reconstitu
*
(mg)
feed
Ready to
100 *
25
1000 * 50*
1000
)
342
180 *(C-D) -B- (A
product
g 100 per
GOS
Amount
:n
calculatio
feed
Ready to
10.5)
(paragraph
(µg/mL)
blank
enzyme
from
galactose
D
10.4)
(paragraph
(µg/mL)
sample
hydrolyzed
- non
from
lactose
C
10.4)
(paragraph
(µg/mL)
sample
hydrolyzed
- non
from
galactose
B
10.3)
(paragraph
(µg/mL)
sample
hydrolyzed
from
galactose
A
:
samples
the of
tion
Quantifica
product)
g 100
GOS/
(g GOS ofn
Calculatio
=
=
=
=
=
+
=
=
=
=
=
=
k
k
d
c
b
a
d
c
b
a
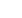
The k-factor (degree of polymerization) is determined as:
n
n
k
⋅
⋅
+
=
180
162
180
where n is the average number of galactose moieties in GOS molecules.
For Vivinal GOS, which is the predominant product on the market, n was determined as 1.71,
which results in a k-factor of 1.485 (Coulier, 2009). We used this k-factor throughout the SLV.
It was not possible to determine the k-factor in IFT samples, for which the GOS source is
unknown.
13.
References:
De Slegte, J. (2002) Determination of trans-Galactooligosaccharides in Selected Food
Products by Ion-Exchange Chromatography : Collaborative Study.
J AOAC Int 85(2)
, 407-423.
Coulier, L. (2009) In-Depth Characterization of Prebiotic Galactooligosaccharides by a
Combination of Analytical Techniques.
J Agric Food Chem 57
, 8488-8495.
GOS-02 SLV
FOR ERP USE ONLY
DO NOT DISTRIBUTE