117
M
ay
2009
www.read-tpt.com›
The mean value of normal errors of every divided point is shown
in figure 7. Given the data of table 1, the maximum error lies in the
edge part of the formed section, and its value is 2.13mm.
According to the fitting curve of the formed section, the curvature
and direction of the normal line can be received. It is possible to
determine the reflection path of the random beam reflected by
formed section. Figure 8 shows the reflection path of the parallel
light with a normal incidence reflected by the formed section and
theoretical parabolic contour.
The adopted samples were precut aluminium sheets; there was an
unavoidable error at the beginning and end of the forming section.
When checking the forming section of the samples, it was decided
to select three cross sections along the forming direction.
The distances from the beginning section were 400mm, 500mm and
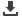
600mm respectively. The detection facilities included a FaroArm
Tumbler trilinear coordinates measuring instrument and one PC with
CAM2 Measure software. The two detection facilities are shown in
figure 5. To ensure that the checked section was normal to the axes
of section, a V-type tank combined fixture was used to orient in the
course of checking.
Discrete points on the section contour were measured by detection
facilities. In this study, discrete points on the section were fitted
by reverse engineering using soft Imageware
and create section
contour curve. Three forming sections of each sample were fitted
and compared with the theoretical parabolic contour. Then, the
symmetrical point of section was used as a coordinate (0, 0), shown
in figure 6.
Because of the symmetry, only the positive half axle of a transversely
unfolding coordinate of section was taken into account. This strip is
divided equally into six parts, and on the divided point, the normal
error between the forming section and theoretical parabolic contour
is shown in table 1.
Table 1
:
A normal error between formed section and theoretical parabolic
contour (mm)
Sample
No.
Formed
section in Z
coordinate
(mm)
Transverse unfolding coordinate of section (mm)
X=0 X=10 X=20 X=30 X=40 X=50 X=60
1
Z=400
0 0.34 0.63 1.24 1.71 1.89 2.03
Z=500
0 0.35 0.69 1.54 1.97 2.06 2.08
Z=600
0 0.32 0.77 1.48 1.92 2.10 2.20
2
Z=400
0 0.27 0.50 1.09 1.62 1.97 2.17
Z=500
0 0.27 0.59 1.26 1.79 2.02 2.18
Z=600
0 0.23 0.49 1.15 1.78 2.02 2.22
3
Z=400
0 0.23 0.45 1.05 1.56 1.84 2.10
Z=500
0 0.32 0.58 1.17 1.68 1.98 2.23
Z=600
0 0.41 0.81 1.48 1.62 1.85 1.99
Figure 3
:
Forming machine used for experiments
Figure 4
:
Formed samples for experiments
Figure 5
:
Detection facility
Transverse unfolding coordinate (mm)
0
0
5
1
5
2
2.5
10
20
30
40
50
60
Normal error (mm)
Figure 6
:
Formed section and theoretical parabolic contour
Figure 7
:
Mean normal error between formed section and theoretical parabolic
contour
Figure 8
:
Collation of
spotlight performance
of formed section and
parabolic contour