power supply are connected in parallel
and both are in current limit for this
measurement.
Figure 5 A DC measurement is made
using precision, low noise 6.5 Digit
DMMs (Picotest M3500A) to obtain a
second measurement for correlation.
The power supply does not have
current programming, which is the
reason the current is set to an odd
number. The two channels of the
power supply are connected in parallel
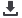
Figure 1, A 250uOhm current
sense resistor is mounted with
RG58 coax soldered directly to the
resistor for measurement
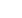
Figure 2 Schematic of the
2-Port impedance measurement
including cable resistance, a
2mOhm DUT and the common
mode transformer
Figure 3 Simulation results of
the 2-port shunt thru impedance
measurement including cable
resistance and 2mΩ DUT with and
without the common mode transformer
Figure 4 Impedance measurement
of the 1mΩ resistor with and
without the J2102A common
mode coaxial transformer using
the OMICRON Lab Bode 100.
and both are in current limit for this
measurement.
The calculated DC resistance value is:
341uV/1.4184A=240uOhms
The noise floor of the measurement
using the J2102A common mode
transformer and a preamplifier is
shown in Figure 6 below. Such a sample
test is important and recommended
as it confirms the validity and limits of
the test setup.
The DMM measured value reflects an
error of 4% from the specified value.
The measurement error includes
the error of the two DC meters and
the 1 Ohm calibration resistor. The
expected error in the measurement
due to the 1 Ohm calibration is:
The measurement of the 250uOhm
resistor is near perfect. Of course
there are other errors, including the
tolerance of the calibration resistor,
the calibration of the two DMM’s and
the gain accuracy of the VNA. There
is also a cable shield resistance error,
60 l New-Tech Magazine Europe