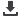
88
Malawi is the most densely populated country
in the Zambezi Basin. Its diverse physical
features support a variety of flora and fauna.
Lake Malawi extends over almost two-thirds of
the eastern border area and with other water
bodies covers one-fifth of the country’s total
area. This extensive water body has a strong
influence on the climate which varies from
semi-arid to humid (SARDC/Chenje 2000).
Progress towards environmental
sustainability
Reverse the loss of environmental resources
Arable land is Malawi`s most valuable natural
resource as agriculture is essential to local
livelihoods and the national economy. The
cultivated area has more than doubled since
1961 to accommodate a rapid growth in
population, resulting in a growing land shortage
(FAO 2007). In 2002, an estimated 16 per cent
of cultivation was taking place on marginal
or unsuitable land (UNEP 2008). This caused
soil erosion, sapping soil fertility and causing
siltation of lakes and rivers, including the Shire
River, which is the major outlet of Lake Malawi.
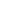
Malawi is on track towards attaining half of
the environmental sustainability indicators,
although the land area covered by forest has
declined from 32.9 percent in 1990 to 27.3
percent in 2010 (Figure 4.17). This decline can be
attributed to fuelwood collection, subsistence
and commercial agriculture (UNEP 2008).
Tobacco farming, which accounts for almost
80 percent of export earnings, is one of the
major causes of deforestation. Government is
committed to reverse this trend by intensifying
reforestation, afforestation, promotion of
natural regeneration, and forest protection and
management programmes.
Deforestation, driven significantly by fuelwood
harvesting and curing of tobacco, is also
contributing to the rapid degradation of
Malawi’s intensively used lands. Malawi is the
second largest tobacco producer in Africa after
Malawi
Total Area of Country
Portion of Country within Zambezi Basin
National Population in 2010
Portion of National Populationwithin Zambezi Basin
Important Environmental Issues
118 484 sq km
110 700 (93.4%)
13.9 million
13 050 000 (96.67%)
• Land scarcity and soil erosion
• Deforestation for fuelwood
• Water pollution
• Aquatic biodiversity
Z
AM
B
E
Z
I
R
I
V
E
R
B
A
S
I
N
LI
M
I
T
Mzimba
Nkhotakota
Salima
LILONGWE
Mchinji
Dedza
Mangochi
Ntcheu
Zomba
Machinga
Blantyre
Mulanje
Mzuzu
Nkhata Bay
Chiromo
Nsanje
Karonga
Chitipa
Lake
Malawi
ZAMBIA
ZIMBABWE
MALAWI
MOZAMBIQUE
MOZAMBIQUE
TANZANIA