90
Malawi’s aquatic resources of over 1 000 fish
species, which make up almost 15 per cent of
global freshwater fish biodiversity, are under
threat from water pollution and overfishing.
Lake Malawi contains more unique fish species
than any other lake in the world, and more than
90 per cent are endemic (CBD 2007), mainly
from the family Cichlidae. The Shire River basin
also has high species richness.
There are 117 species in Lake Malawi assessed
as vulnerable due to highly restricted
distribution, in some cases these species may be
restricted to a section of rocky shore of less than
a few hundred metres in length. Such species
are assessed as vulnerable due to risks that may
eliminate entire populations given their highly
restricted ranges (IUCN 2011).
Malawi is also rich in biodiversity of birdlife, and
the major wildlife groups of mammals, reptiles
and amphibians are represented, but the number
of threatened species recorded almost doubled
between 1996 and 2003, to 41 (IUCN 2006).
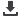
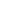
Access to safe drinking water and improved
sanitation by 2015
According to the Malawi Development Goals
Report 2009, the country has already surpassed
the MDGs targets for access to clean water and
improved sanitation, and is well on its way to
achieving 100 per cent for the latter (Figures
4.20 and 4.21).
Improve the lives of slum dwellers by 2020
The slum population as a proportion of total
urban population in Malawi has been reduced
by almost 30 per cent since 1990, from 94.6
per cent to 66.4 per cent, and is projected to
reach 64.57 per cent by 2015, according to UN-
Habitat (2010) as shown in Figure 4.22.
Malawi remains committed to achieving what
it calls the Malawi Development Goals (MDGs)
by 2015 through implementation of a national
development plan called the Malawi Growth
and Development Strategy (MGDS). The first
Strategy covered the period 2006 to 2011, and a
successor MGDS was being designed to replace
it (Government of Malawi 2009).
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
1990 1995
2000
2005
2010 2015
Percentage
Households with sustainable access
to improved water source in Malawi
MDG Target Current Path Linearly Projected Value
Source: Government of Malawi 2009
0
20
40
60
80
120
100
1990 1992 1994 1996 1998
2004 2006 2008 2010 2012
Percent
Proportion of populationwith access to
improved sanitation facilities inMalawi
2000 2002
MDG Target Current Path Linearly Projected Value
Source: Government of Malawi 2009
50
60
70
80
90
100
1990
2000
2005
2010
2015
Percent
Urban dwellers living in slum
conditions in Malawi
Current Path Linearly Projected Value
Source: Government of Malawi 2009
Figure 4.21
Figure 4.20
Figure 4.22