13
Zambezian Biome
The Zambezian biome covers 95 per cent of
the basin, and comprises woodland, grassland,
swamp and lakes (Timberlake 2000). The climate
has distinct seasons with marked dry and wet
seasons. This biome is sometimes subdivided
into moister areas characterized by broad-
leaved miombo (
Brachystegia
) woodland, and
drier areas with mopane (
Colophospermum
mopane
) and/or Acacia or wattle woodland.
The Zambezi basin is home to more than
6 000 species of flowering plants, 650 species
of birds and 200 species of animals (Timberlake
2000). In addition, 165 species of freshwater
fish are recorded in the basin and more than
500 endemic species (mostly cichlids) in Lake
Malawi/Nyasa/Niassa (SARDC IMERCSA 2003).
Montane Biome
The Montane biome lies between 1 800 and
2 000 metres above sea level. It is cooler, wetter,
often shrouded in mist, and has a much more
temperate climate. Species found in this biome
include grassland herbs and introduced species
such as pine and wattle trees (Chenje 2000).
The Congolian Biome
The Congolian Biome is within the head waters
of the Zambezi in northwestern Zambia and
northeastern Angola. The biome has a moister
and warmer climate than the rest of the plateau
portion of the basin. The vegetation and wildlife
species are a mix of those found in the forested
Congo Basin and in the less tropical, more
wooded Zambezi basin (Chenje 2000).
   
Coastal Biome
The coastal biome is the small part of the basin
in Mozambique where climate is modified by
proximity to the coast, the delta area and its
Biodiversity
The Zambezi River Basin is rich in biodiversity
and includes four distinct biomes; the
Zambezian, Congolian, Montane, and Coastal
(Chenje 2000).
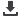
The Yellow Billed Stork is one of the many birds found
in the Zambezi basin.
© Antonio Klaus Kaarsberg
© Antonio Klaus Kaarsberg