www.read-tpt.com
www.read-tpt.com
January
2014
103
Steel Plant Specialities
Article
Steel Plant Specialities
– India
Tel: +91 22 67978060
Fax: +91 22 25552459
Email:
info@steelplantspecialities.comWebsite:
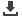
www.steelplantspecialities.com4. Heat treatment of pressure vessels
Valve areas of pressure vessels are critical
and need to be protected from scaling during
thermal cleaning and heat treatment. This is
achieved by use of anti-scale coating being
applied only on areas where scaling needs to
be prevented (Image 3).
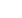
5. Salvaging of rejected forgings
Re-heating or re-working of forgings is
required due to underfill, improper metal
formation and similar reasons. However,
with stringent dimensional tolerances, there
is a risk of components getting scrapped
due to excessive scaling (Image 4). Anti-
scale coating, when applied on forgings before
re-heating for re-working, ensures minimal or
no scaling, thereby eliminating risk of scrapping
components during re-working (Image 5).
6. Reducing decarburisation during hot
forging and hot rolling
During hot rolling of special grades of steel
where decarburisation needs to be kept in
check, unforeseen conditions like mill
breakdown and unplanned downtime may
arise. Even when the plant is closed for weekly holiday, the
furnace is shut off abruptly, leaving billets inside the furnace.
In these cases, billets or ingots are left in furnace and are
subjected to prolonged heating leading to decarburisation. In
both cases, applying an anti-scale coating ensures that billets
are protected from decarburisation. (Endorsements 3 & 4)
Summary
1. Use of protective coating has established itself as
an effective technique of preventing oxidation and
decarburisation during heat treatment, hot forging and hot
rolling.
2. It has unleashed a number of additional benefits like ability
to salvage by re-heat treatment, elimination of post-heat
treatment operations like grinding, shot blasting, acid
pickling, etc.
3. The coating process has simplified and accelerated many
metallurgical heat treatment operations, saving a fortune
in capital investment, reducing costs and improving quality.
Image 3
: Protection of critical valve areas during heat treatment of pressure vessel.
Coating was applied on critical areas that have turned white after heat treatment,
with zero scaling
Image 4
: Pit marks formed due to scaling during re-heating for
re-working
Image 5
: Coated with ESPON anti-scale compound before
re-heating. No scale pit marks