Wafer-level
chip
scale
packages
are
allowing
designers
of
portable
healthcare equipment - such
as invasive sensing, medical
implants, and disposable
monitors - to reduce size and
power requirements.
ne of the key trends in medical
equipment design is to bring
equipment closer to patients at the
doctor’s office or at their own home by
making these devices more portable.
This involves all aspects of the design,
but especially effects size and power
consumption. Shrinking the electronic
portion of these instruments is being
aided greatly by the use of wafer-level
chip-scale packages (WLCSPs).
These new applications include
invasive sensing, medical implants,
and disposable, portable monitors.
But to get the most out of WLCSPs in
terms of performance and reliability,
designers should heed the best
practices in designing the printed-
circuit board (PCB) land pattern, pad
finish, and board thickness.
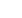
Wafer-level chip scale packaging is a
variant of the flip-chip interconnection
technique (Figure 1). With WLCSPs,
the active side of the die is inverted
and connected to the PCB using solder
balls. The size of these solder balls is
typically large enough (300 μm pre-
reflow for 0.5-mm pitch, and 250 um
pre-reflow for 0.4-mm pitch) to avoid
the underfill that is required for flip-chip
interconnects. This interconnection
technology offers several advantages.
First, considerable space savings are
obtained by eliminating the first level
package (mold compound, lead frame,
or organic substrate). For example, an
8-ball WLCSP occupies only 8% of
the board area taken up by an 8-lead
SOIC. Next, inductance is reduced and
electrical performance is improved by
eliminating the wire bonds and leads
used in standard plastic packages.
Also, designs yield a lighter weight
and thinner package profile, due to
the elimination of the lead frame and
molding compound. No underfill is
required, as standard surface-mount
(SMT) assembly equipment can be
used. And finally, high assembly
yields result from the self-aligning
characteristic of the low mass die
during solder attachment.
Package Construction
WLCSPs can be categorized into two
construction types: direct bump and
redistribution layer (RDL).
A direct-bump WLCSP consists of an
optional organic layer (polyimide),
which acts as a stress buffer on the
active die surface. The polyimide
Chip Scale Packaging Helps Portable Medical
Devices Save Size and Weight
Mike Delaus and Santosh Kudtarkar, Analog Devices, Inc.
34 l New-Tech Magazine Europe