depends on the required robustness of
the populated system assembly. The
thinner board results in smaller shear
stress range, creep shear strain range,
and creep strain energy density range
in the solder joints under the thermal
loading. Hence, the thinner buildup
board would lead to a longer thermal
fatigue life for solder joints.
Testing and Assessment
In conjunctionwith the aforementioned
variables, WLCSP reliability is assessed
by subjecting the device to accelerated
stress tests such as high temperature
storage (HTS), highly accelerated
stress testing (HAST), autoclave
testing, temperature cycling, high
temperature operating life testing
(HTOL), and un-biased highly
accelerated stress testing (UHAST).
In addition to thermo-mechanical
induced stress testing, mechanical
tests such as drop and bend testing
are also carried out.
HTS testing is performed to determine
the effect of long-term storage on
devices at elevated temperatures
without any electrical stresses
applied. This test assesses the long-
term reliability of devices under high
temperature conditions. The typical
test conditions are 150°C and/
or 175°C for 1000 hours. This test
consists of exposing the parts at the
specified ambient temperature for a
specified amount of time.
RESOURCES
For further information on healthcare
applications, visit our site.
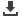
Figure 3. Redistribution Layer (RDL) WLCSP
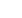
Figure 4. Pad Opening
Figure 5. Pad Type
Internet-of-Things Board
ARIS
New-Tech Magazine Europe l 37