Ten Year Network Development Plan 2015 |
187
-8
6
2
4
0
-2
-6
-4
%
2015
2020
2025
2030
2035
RU
LNG
NO
DZ
LY
AZ
LOW – Grey Scenario
Expensive
Cheap
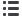
Figure 6.36:
Influence of the gas price scenario in the European gas bill (towards the reference gas price).
Green and Grey scenarios
-8
6
2
4
0
-2
-6
-4
%
2015
2020
2025
2030
2035
RU
LNG
NO
DZ
LY
AZ
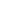
HIGH – Grey Scenario
Expensive
Cheap
-8
6
2
4
0
-2
-6
-4
%
2015
2020
2025
2030
2035
RU
LNG
NO
DZ
LY
AZ
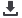
LOW – Green Scenario
Expensive
Cheap
-8
6
2
4
0
-2
-6
-4
%
2015
2020
2025
2030
2035
RU
LNG
NO
DZ
LY
AZ
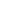
HIGH – Green Scenario
Expensive
Cheap
-8
6
2
4
0
-2
-6
-4
%
2015
2020
2025
2030
2035
RU
LNG
NO
DZ
LY
AZ
LOW – Grey Scenario
Expensive
Cheap
In line with the rest of TYNDP assessment, the European gas bill is most sensitive to
LNG and Russian supplies. Norway’s influence is rapidly limited by its decreasing
export potential. Non-FID projects, taken into account in the High scenario, have the
potential to limit the gas bill increase by giving access to the cheapest sources.
6.5.2 GAS PRICE INDEX
The Gas Price Index (GPI) is calculated as a proxy for the gas bill per unit of gas
demand and hence allows Zones to be compared which have different market sizes.
At TYNDP level, the analysis of the index provides a common background to the
monetization measure within the Project Specific-Step of the CBA. It is not the
central indicator of this report as most of the information provided is illustrated by
other indicators.
The main drivers for the evolution of this index at Zone level are:
\\
The overall impacts of new projects and associated supply decreasing the
European gas bill
\\
The impact of projects enabling a wider spread of the price impact of the
cheapest source
\\
The impact of projects mitigating the influence of the most expensive source
In addition when a source is considered as more expensive (higher price curve),
countries are taking more of the alternative sources resulting in an increase of their
price (see price curve profile in Annex F). This indirect effect of any price configu-
ration participates to the impact on distant countries from the expensive source.