11
80
180
180
230
280
1900
1910
1920
1930
1940
1950
1960
1970
1980
1990
2000
Index reference: 1977-1979 = 100
1917
Just before World War I
1951
Rebuilding after World War II
1974
Oil crisis
2008 forecast
80
100
120
140
160
180
200
FAO Food price index (FFPI)
The current world food crisis is the result of the combined effects of competition for crop-
land from the growth in biofuels, low cereal stocks, high oil prices, speculation in food
markets and extreme weather events. The crisis has resulted in a several-fold increase in
several central commodity prices, driven 110 million people into poverty and added 44
million more to the already undernourished. Information on the role and constraints of
the environment in increasing future food production is urgently needed. While food
prices are again declining, they still widely remain above 2004 levels.
The objective of this report is to provide an estimate of the potential constraints of envi-
ronmental degradation on future world food production and subsequent effects on food
prices and food security. It also identifies policy options to increase food security and
sustainability in long-term food production.
CURRENT WORLD FOOD CRISIS
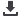
Figure 1: Changes in the prices of major commodities from 1900 to 2008
reveal a general decline in food prices, but with several
peaks in the past century, the last and most recent one the most extreme. (Source: World Bank, 2009).