5
Central South
Atlantic
West
Africa
Mediterranean
Sea
Central
Africa
Eastern
Africa
Southern
Africa
Mainland
Southeast Asia
Papua
New Guinea
Russia
Arafura
Sea
Western
Central Pacific
g
Western
Europe
Indonesia
Japan
Golden
Crescent
China
Myanmar
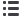
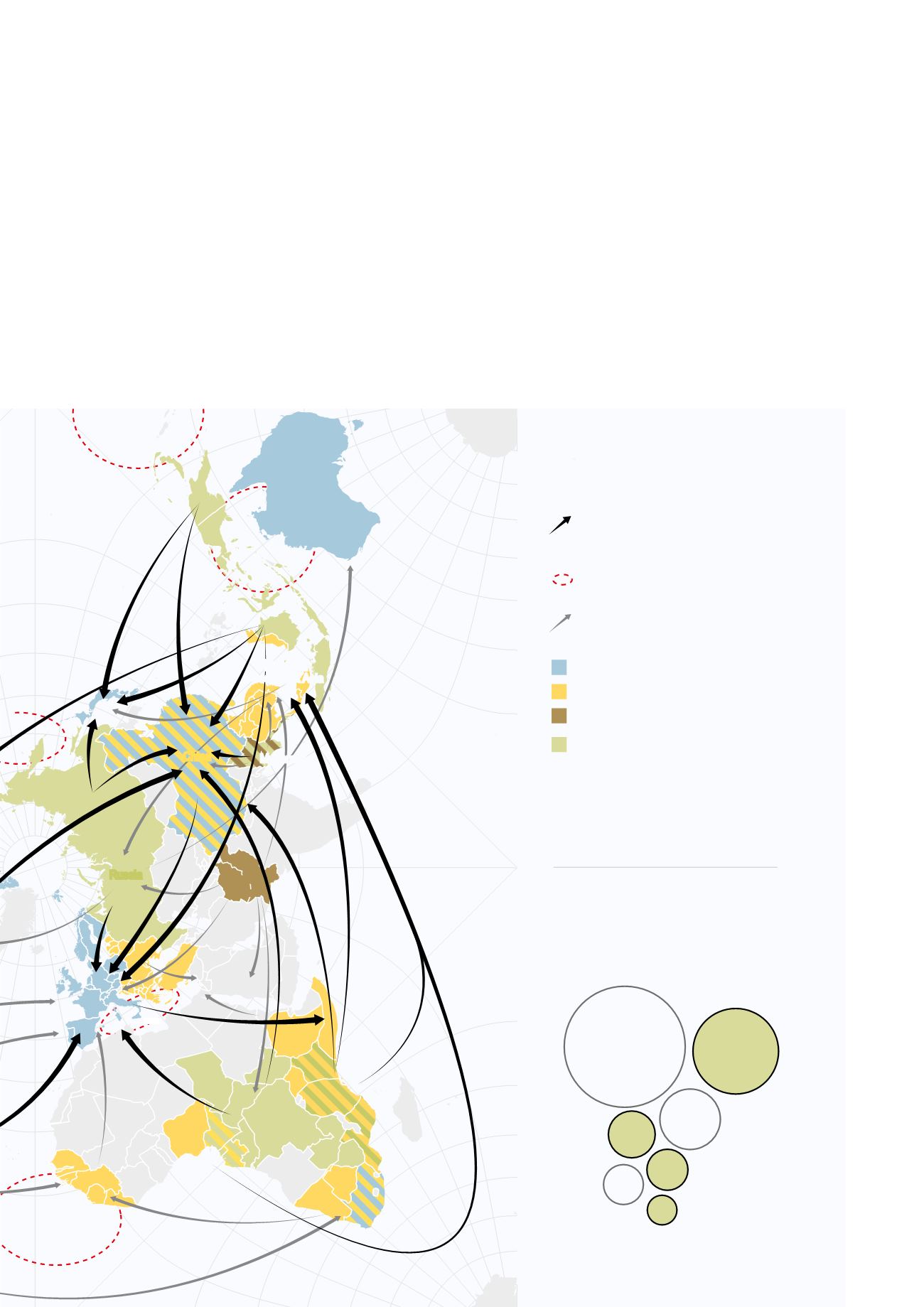
New and old trafficking routes
Environmental crime network
Drugs
E-crimes
Illegal
fishing
Illegal trafficking
of toxic wastes
Wildlife trafficking
200
50
100
30
23
12
20
Illegal logging and
trafficking
Annual revenue, higher estimates
Billion dollars
A growing sector
Illegal
trafficking of
light weapons
“Traditional” illegal trafficking.
Includes heroin, cocaine and
human beings
Main destination country
Main transit country
Country of origin of “traditional”
illegal trafficking
Main country or region of origin of
environmental related illegal trafficking
Environment-related illegal trafficking.
Includes wood, wildlife, animal parts
(i.e.ivory, rhinocerous horns and fur) and
wastes
Main illegal, unreported and
unregulated fishing areas
Sources: UNODC Annual Reports 2010 e 2013;
WWF-Australia;
Globaltimber.co.uk,Estimates of the
percentage of “Illegal Timber” in the imports of wood-based
products from selected countries, 2007; TRAFFIC; FAO;
World Ocean Review Report 2013; Michigan State
University, Human Trafficking Task Force; Greenpeace, The
Toxic Ship, 2010; National Geographic press review.
Sources: TRAFFIC; FAO; UNODC;
Global Financial Integrity
The Environmental Crime programme
1
expanded in
2014 to cover illegal waste trade, illegal fisheries, illegal
logging and the poaching of wildlife and other resources.
Developed jointly with the UN Office on Drugs and Crime
(UNODC), the International Criminal Police Organization
(INTERPOL), and the Convention on International
Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora
(CITES), the programme is funded by a range of donors.
It supports national and international law enforcement
initiatives to combat transnational crime, mainly through
the development of better information and analysis
techniques, preparation of practical manuals and field
training for detection and enforcement personnel.
1. Environmental Crime
Illegal trade in wildlife was a major topic of the Ministerial
discussions of the first United Nations Environment
Assembly (UNEA) in June 2014. GRID-Arendal provided
substantive input to the Information Document for
these discussions.
2
Along with INTERPOL and UNEP, it
released a Rapid Response Assessment (RRA) report,
The
Environmental Crime Crisis
. The report highlights how
environmental crime is used to finance criminal, militia
and terrorist groups and how it threatens human security
and sustainable development.
The report was a major news story with over 2000 news
articles published in 112 countries around the world.