3/9/2017
1
AOAC Official Method 2014.09
Determination and Confirmation of Residues of 653 Multiclass Pesticides
and Chemical Pollutants in Tea GC-MS, GC-MS/MS, and LC-MS/MS First
Action 2014
130th AOAC INTERNATIONAL Annual Meeting And Exposition
AOAC Expert Review Panel for Pesticide Residues
September 21, 2016 Dallas, TX
Research background: development of the analytical technique for multi-residues in tea
becomes imperative.
•
Background and History
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
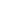
8
493
270
81
13
24
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
美国 欧盟 日本 德国 CAC
中国
USA EU Japan Germany
C China
(
2001
)
(
2010
)
(
2010
)
(
2001
)
(
2009
)
(
2005
)
Sourceof literature
:http://ec.europa.eu/sanco_pesticides/public/index.cfm http://www.m5.ws001.squarestart.ne.jp/foundation/search.html http://www.tbtsps.com/foodsafe/xlbz/Pages/pesticide.aspxGB2763-2005
DoctoralDissertationofAnhuiAgriculturalUniversityWuXueyuan MRL ofPesticides inTea andRiskEvaluation
8
81
13
24
270
493
The threshold of limit for pesticide residues in tea is high for international trade. At present, there are 17 countries
and international organizations that have stipulatedMRL levels for over 800 pesticide residues in tea*.
The high threshold of international trade from limit of pesticide residue in tea
*EU, Germany, Holland, Switzerland, Hungry, Israel, CAC, China, Japan, Chinese Taiwan, Korea, USA, Australia, India, Kenya and SouthAfrica
(till 2006).
2