4-15
Go to Chapter Start-
Table of Contents-
IndexEvaporator Coil
Evaporator Coil
Evaporator coils come in various shapes and sizes. Most are of fin and tube
construction. The fins and tubing are designed to transfer heat from the cab air
to the cool refrigerant vapor as it moves through the evaporator tubing. The
fins are colder than the cab air, so moisture in the air blown across the coil
condenses on the fins. The moisture forms into droplets and drains to the
bottom of the evaporator housing and out of the cab through a drain tube. Dust
or other airborne particles may also be trapped in the condensed moisture
droplets. In this way the AC system dehumidifies, filters and cools the air in the
cab.
Refrigerant enters the evaporator coil, expands rapidly and changes state
(drops in temperature and pressure). The refrigerant absorbs heat energy from
the air in the cab and moves through the tubing to exit the evaporator coil. A
variety of expansion valve or other refrigerant flow regulating devices (de-
scribed earlier) are used in an AC system design, at the inlet to and/or the
outlet from the evaporator coil. Each is designed to control the flow of refriger-
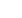
ant to provide maximum heat transfer in the evaporator. The drawing, Figure
4-12, is a cutaway view of a typical evaporator coil.
EVAPORATOR
EXPANSION VALVE
COLD LOW PRESSURE GAS
THERMOSTAT
METERED REFRIGERANT
CAB AIR
FLOW
Air Conditioner Blower/Fan and Motor Assembly
In HVAC system designs, a blower assembly is positioned to move air through
the evaporator coil and heater core. For efficient air movement, the air must be
confined within a housing. The blower assembly used in a system may be
located for functional or space considerations. Some pull air and others push
air through evaporator and/or heater fins.
Fans are used to move air through the fins of the condenser. In underhood
applications the engine cooling fan is used. Roof or remote mounted condensers
have separate fan/motor assemblies.
Figure 4-12
The evaporator coil illus-
trated is mounted inside an
enclosure (not shown) de-
signed for efficient air flow
between the fins of the
evaporator.