48 |
Southern Corridor GRIP 2017–2026
0
25,000
20,000
15,000
5,000
10,000
40,000
35,000
30,000
GWh/y
2010
2009
2012
2011
2013
2014
2015
Nuclear
Coal & Lignite
Oil
Biodegradable waste
Biomass
Other Energy sources
Hydro
Natural gas
Biogas
Solar
Waste
Wind
Figure 3.16:
Power generation of Hungary by source (historical)
0
3,500
3,000
2,500
1,000
500
1,500
2,000
5,000
4,500
4,000
GWh/y
2017
2016
2019
2018
2020
Nuclear
Coal & Lignite
Oil
Biodegradable waste
Biomass
Other Energy sources
Hydro
Natural gas
Biogas
Solar
Waste
Wind
Figure 3.17:
Forecast of power generation in Hungary from
Renewable Energy sources from 2016 to 2020
10)
0
200,000
150,000
100,000
50,000
350,000
300,000
250,000
GWh/y
2011
2010
2013
2012
2014
2015
Solar
Wind
Hydro
Biomass & Waste
Oil
Geothermal
Pumps
Natural gas
Other fossil fuels*
Coal & Lignite
* includes e. g. derived gases, heat recovery and compressed gas expansion
Figure 3.18:
Power generation in Italy by source (historical)
(Source: Terna)
3.5.4 HUNGARY RENEWABLES
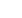
The Figure 3.16 shows split among the sources used for power generation in
Hungary during the recent years. Figure 3.17 presents the forecasted evolution in
the use of renewable sources for power generation in Hungary.
10)
3.5.5 ITALY POWER PRODUCTION
(INCLUDING RENEWABLES)
Figure 3.18 shows the evolution of electricity
production and of the shares of the various energy
sources used for power generation, in Italy, for the
period 2010–2015.
Renewable sources in Italy experienced a steady
growth, during the last years, reaching in 2015
38% of the total power production. Hydroelectric
production covers around 40% of RES share,
followed by solar energy which accounts for
around 8% out of the total production.
Anyway, other fuels are expected to keep a key
position in the Italian electricity balance,
accounting for more than 60% of the electricity
production. In particular, gas is by far the first
among other fuels, covering in 2015 38% of the
total production, followed by coal with 15% and
oil, both in progressive decrease (complete phase
out from coal is proposed for 2030).
10) Source: Hungary’s Renewable Energy Utilisation Action Plan