46
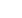
Figure 3.4 Elements of the PMMS
Within the PMMS two levels or elements can be differentiated (see Figure 3.4):
• The performance measurement Instruments and/or tools are used to measure
and document the performance of the business system. Especially KPIs can
be subsumed here but also other, more complex instruments such as the total
cost of ownership or balanced scorecards (BSC) can be used to measure the
performance. Those instruments are aimed at capturing the performance of
the business system in a reliable and valid way to form the basis for the
management to make good decisions. They should therefore map the
performance in a holistic way, covering all relevant aspects of the business
system. Often the instruments themselves consist of different elements,
performance measures or indicators. In a respective instrument, they are
linked to each other in a certain way. For example, in a BSC, they are grouped
into four different categories based on a certain linking-logic.
• The performance management process is the link between the management
system and the business system. It has to make sure on the one hand that
developments in the business system are detected and addressed to the
management and on the other hand that impulses frommanagement decisions
are effectively implemented. This can be done on the basis of the PDCA-cycle
or other processual structures. The process should also make sure that external
sources of information such as benchmark data or stakeholders’ requirements
are appropriately integrated in the goal setting and evaluation.
To design a suitable PMMS for sustainability in supply chain management the following
questions are addressed in the following chapters:
• What are guidelines to form good and modern PMMS on the different levels
(single performance elements, performance measurement instrument/tool
and performance management process)?
• Which aspects of performance should be addressed in the performance
indicators for sustainable supply chains?