Compiled by the authors from various sources
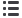
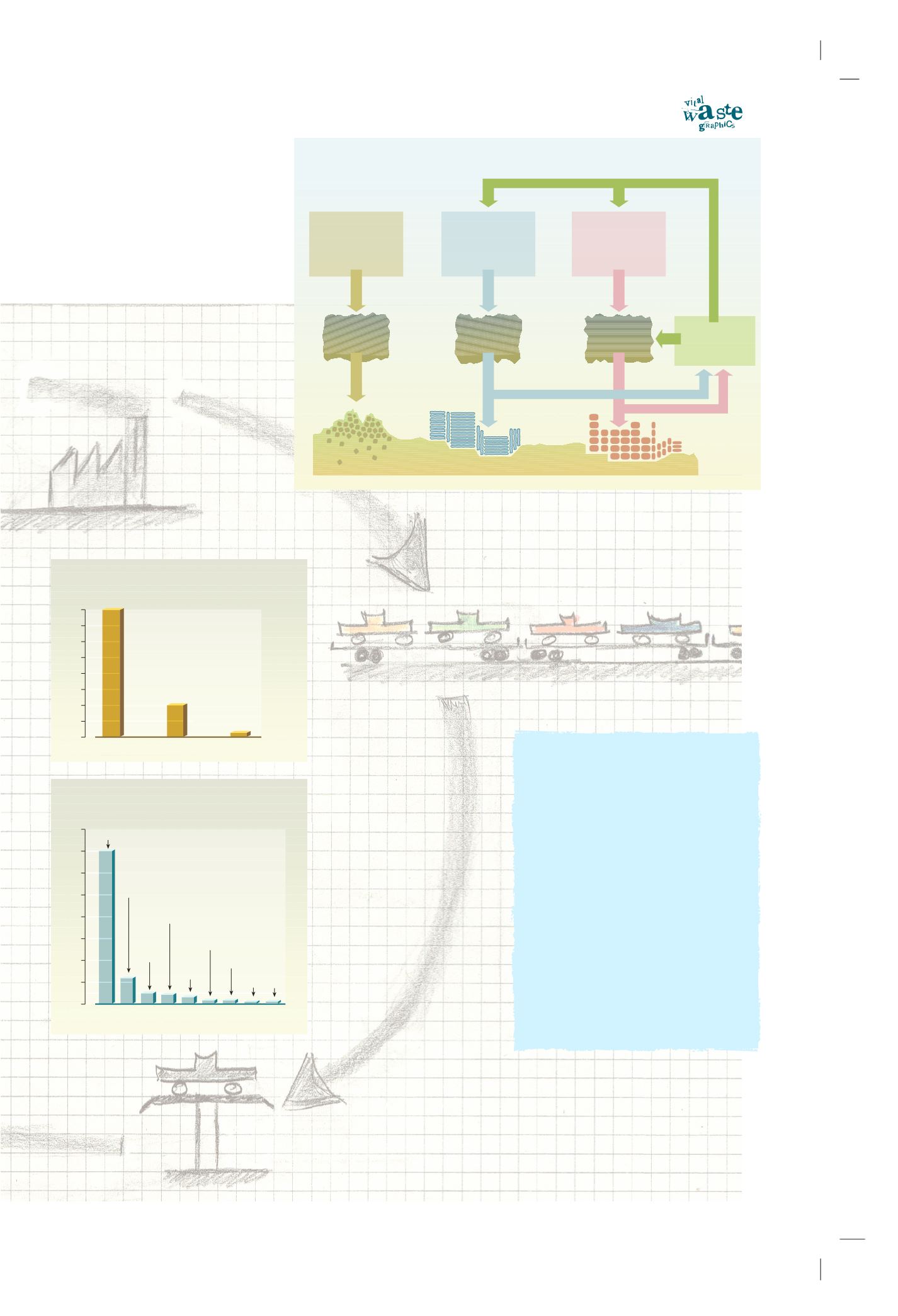
Waste generation scheme
W A S T E M A N A G E M E N T - C O L L E C T I O N
W A S T E M A N A G E M E N T
Final
disposal
Final
disposal
Final
disposal
E A R T H
Raw
material
extraction
Production
Manufacturing
Processing
Formulation
Distribution
Consumption
Use
Maintenance
Waste
Waste
Waste
Re-use
Recycling
Recovering
Renewable and
non-renewable
resource supply
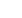
80
50
40
10
70
60
30
20
0
In percentage
8 000
4 000
2 000
0
In kg
6 000
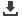
What is a car made of ?
Foam and
cables
1%
Lead
1%
Aluminium
2%
Non-ferrous metal
Brass, copper, zinc
2%
Glass
3%
Gas, oil and grease
4%
Rubber
5%
Synthetic material
and plastics
12%
Steel and iron, all sorts
70%
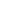
Raw material residues
8 000 kg
Waste as a result of car production
Copper, nickel
and other residues
175 kg
Waste rocks
2 000 kg
Source : OFEFP, 2003.
Source : OFEFP, 2003.
10
11
Production:
During the final assembly: paints, coatings,
lubricants and fluids (generating excess
materials – a specific type of waste)
Distribution:
Assembled cars are transported by truck, train and
cargo to dealerships (generating air emissions).
Factories, assembly plants, road systems, parking
places, dealerships and garages require land to be
cleared, resulting in deforestation, degradation of
habitat for wildlife and an increase in rainwater runoff.
Consumption:
Maintenance and repair of cars generates a large
range of hazardous waste: fuel, oil, lubricants,
washing powder, wax, paint, rubber (tires), tar,
anti-freeze liquid and other products such as acids
and chemicals (used in batteries, air-conditioning
systems, brake systems).
Ecologic review for a 1 000 kilogram car
produced in 1994; estimated over 10
years; assuming a total mileage of
150 000 kilometers and an average fuel
consumption of 8.1 liters per hundred
kilometers.
From production to disposal of the car
Energy produced and used
for the extraction of raw materials
for the production of the car
for running the car during its life time
Air emissions
Carbon dioxide
Carbon monoxide
Volatile organic compounds (VOC)
Sulfur dioxide
Nitrogen oxides
6%
4%
90%
36 000 kg
413 kg
192 kg
34 kg
28 kg