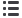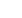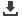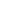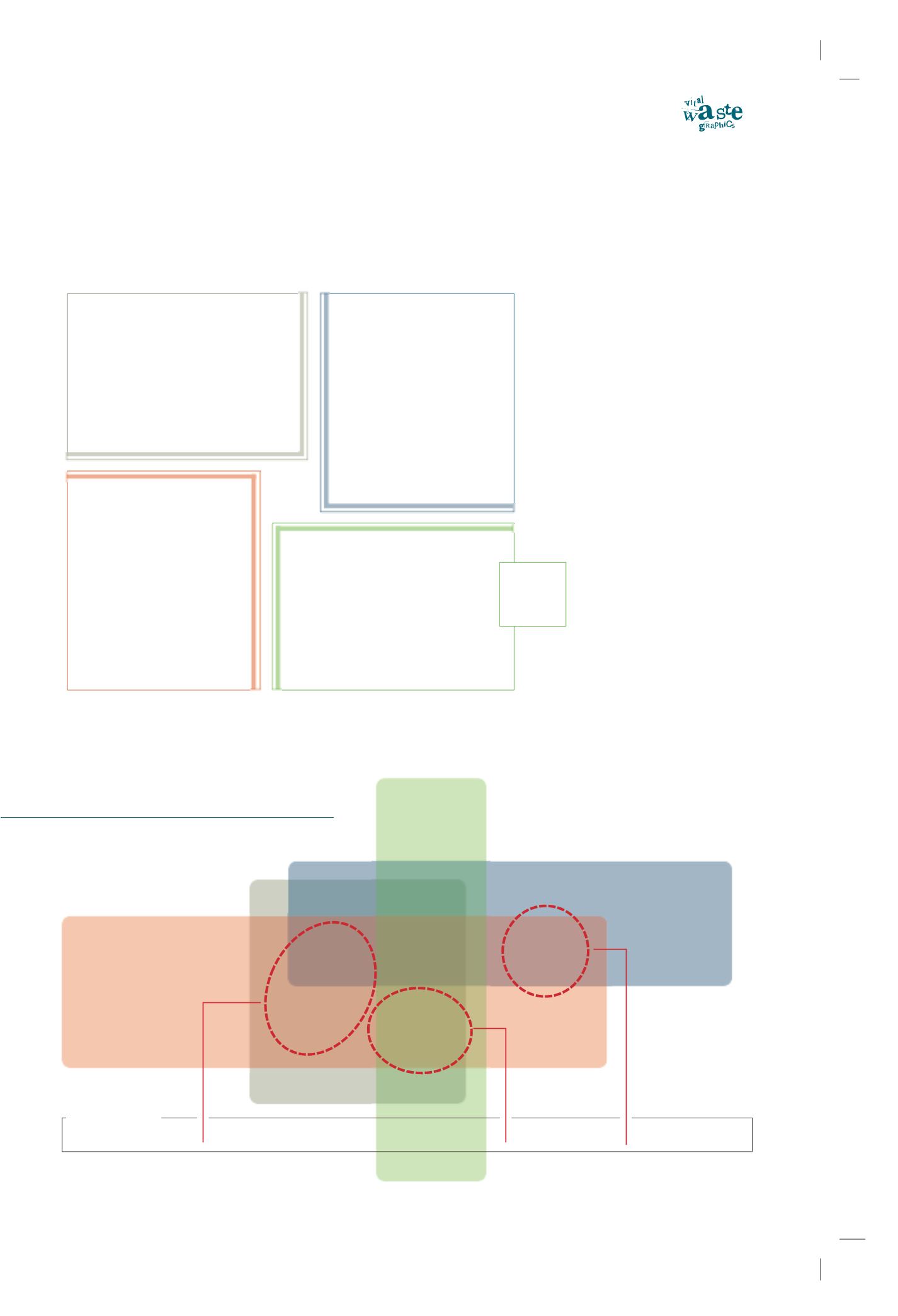
Overlapping Definitions
clinical wastes
pharmaceutical
waste
Origin
Composition
Management
Toxicity
Compost
e-waste
logging waste
waste-rock
Hazardous waste streams
Wastes requiring
special consideration
BASEL CONVENTION
WASTE CLASSIFICATION
Wastes containing
(having as constituents)
NB: in the following pages the boxes contain examples not exhaustive lists.
radioactive
waste
sewage
sludge
wood
preservatives
household
waste
arsenic
cyanides
cadmium
household waste
incineration residues
organic solvents
phenols
6
7
Waste disposed of
(deep-well, surface disposals..)
Poisonous
Corrosive
Ecotoxic
Infectious
Different approaches
Management
Municipal waste Urban waste
Solid
waste
Waste collected
how is waste handled? who is in charge?
sorted
recycled
composted
incinerated
landfilled
Origin
Extraction
waste
Manufacturing
waste
Nuclear
waste
Agricultural
waste
Military
waste
Medical
waste
what human activities generate waste?
Sewage sludge
Garbage
Yard trimmings
Recycling
waste
Industrial
waste
Tailings
Toxicity
Radioactive
POPs
Hazardous vs.
non-hazardous waste
how dangerous is it for human health
and the biosphere?
Toxic
Dangerous
waste
Special
waste
Stabilized waste
Composition
Plastics
Organic waste
Glass
Paper
Packaging
waste
Metal
Mercury
Cyanides
Lead
what is waste made of?
Wood
Textile
Bulky waste
Food
waste
Ashes
TOTAL
WASTE
Waste reduced
Waste water
Explosive
Flammable
Tyres
Pesticides
Dirt
Waste
stored
Life cycle
approach :
waste as a
resource
Waste
transported
sold
dismantled