Technical article
January 2017
50
www.read-eurowire.comvalues at -40°C, at 1,310nm and 1,550nm
wavelengths respectively.
After the test, attenuation changes of
all fibres are really small and no visual
damage to the cable sheath has been
found.
5 Conclusion
When
micro-duct
air-blown
cables
are used in cold areas, the influence
of freezing condition on optical fibre
transmission should be taken into
consideration. In order to study this
subject, two experiments are designed to
evaluate such influence.
Based on the test results in this paper, it
can be concluded that the effects of frozen
water on micro-duct air-blown cables are
insignificant.
However, the long-term effect during the
cable lifetime should be also considered
and further investigated. Thus, protective
measures to avoid the penetration of
water into micro-ducts should not be
ignored.
n
6 References
1 IEC 60794-1-22 Optical fibre cables – Part 1-22:
Generic specification – Basic optical cable test
procedures – Environmental test methods
2 IEC 60794-5-10 Optical fibre cables – Part
5–10: Outdoor microduct optical fibre cables,
microducts and protected microducts for
installation by blowing
Paper courtesy of the 64
th
IWCS Technical
Symposium, Atlanta, Georgia, USA, October
2015.
Yunfang Ruan, Zhuang Xiong,
Xiaoli Liu, Wenjing Ye
State Key Laboratory of Optical Fibre
and Cable Manufacture Technology,
Yangtze Optical Fibre and Cable Joint
Stock Co Ltd, and Huawei Technologies
Co Ltd
Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Wuhan, Hubei, China
Tel
: +86 27 67887520
:
xiongzhuang@yofc.com▲
▲
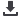
Figure 5
:
Water frozen around end caps
▲
▲
Figure 6
:
OTDR graphs of the fibre with the largest
attenuation values at -40ºC during the end cap test