75
Figure 3.4
Lake Malawi/
Niassa/Nyasa
Lake Cahora Bassa
Chavuma
Zambezi town
Mongu ferry
Kalongola-
Senanga
Kazungula
Caia
Katima Mulilo
Nmawala
(Kafue Flats)
Luang-
Kanyembawa
Lake Kariba
NAMIBIA
ANGOLA
BOTSWANA
ZAMBIA
ZIMBABWE
MOZAMBIQUE
TANZANIA
MALAWI
L
u
n
g
u
e
B
u
n
g
o
Z
a
m
b
e
z
i
C
u
a
n
d
o
Z
a
m
b
e
z
i
K
a
b
o
m
p
o
L
u
a
n
g
w
a
M
a
z
o
e
S
h
i
r
e
S
h
a
n
g
a
n
i
K
a
f
u
e
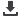
Zambezi River Basin navigation system
Downstream of Cahora Bassa Dam, Zambezi River used
to transport local molasses and construction materials,
as well as supporting coal mining at Moatize
Ferry crossing
Bridge
Lake navigation
Source: World Bank 2010. The Zambezi River Basin, A Multi-Sector Investment
OpportunitiesAnalysis.Volume3,Stateof theBasin. IBRD/WorldBank,WashingtonDC.
SADC and ZRA 2007. Rapid Assessment Report: Integrated Water Resources
ManagementStrategy for theZambeziRiverBasin.SADCWaterDivision,Gaborone.
Ferries are one of the main means of transport on navigable sections of the Zambezi basin.
Navigation in the Zambezi Basin
Navigation on the Zambezi River is both
international and local. The main international
transport routes are the Kazungula and
Luangwa-Kanyemba, while major national
routes are in the upper Zambezi River and
on Lake Malawi/Niassa/Nyasa. There are also
small crossings that provide access to major
markets (Denconsult 1998). There are major
crossings on the Kabompo River, Kafue River
and Chobe River in Namibia and Botswana, and
on the Shire River in Mozambique and Malawi.
Tanzania, Malawi and Mozambique, which share
Lake Malawi/Niassa/Nyasa, all use the lake for
navigation (Denconsult 1998). The section of the
Zambezi running 570 kilometres fromMphanda
Nkuwa, Mozambique to the Indian Ocean is
the longest navigable portion of the river. Coal
was transported in barges along the river in the
1940s and molasses in the 1970s. Construction
materials for the Cahora Bassa Dam were also
transported in barges up to Mphanda Nkuwa
in the 1970s. New projects in the region may
require transportation of materials by river and
lake navigation. These include coal mining in
Tete, the rehabilitation of Sena Sugar Estates
in Mozambique, and the construction of the
Mphanda Nkuwa River Dam (SADC 2000).
On Lake Kariba, a ferry provides the main
transport system linking Binga and Kariba in
Zimbabwe. On the Zambian side another ferry
operates between Siavonga and Chepepo, and
Siavonga and Shenga. In Zambia, a number
of other ferries operate on the Zambezi River
at Chavuma, Ngoma, and Sandaula/Malumbu
in Mongu, Katima Mulilo/Shesheke, and
the Kalongola/Senanga. In Lukanga, water
crossings exist between Chilwa Island and
Chitanda. Other crossings are at Caia and
Songo in Mozambique
© Bernhard Richter/Dreamstime.com