80
Total Area of Country
Portion of Country within Zambezi Basin
National Population in 2010
Portion of National Populationwithin Zambezi Basin
Important Environmental Issues
1 246 700 sq km
256 500 sq km (20.5%)
17.8 million
651 480 (03.66%)
• Biodiversity loss
• Access to potable water
Although the Zambezi River rises in Zambia, part of
its upper course is in northeastern Angola, which
is the seventh largest country in Africa by area and
has an Atlantic coastline of 1 650 km. The country
has distinct and alternating rainy and dry seasons,
and is semi-arid in the South and along the coast
to the capital, Luanda.
Oil is at the core of the Angolan economy and
the sector contributes more than 90 per cent
of national exports (AfDB 2010). Other mineral
resources include diamonds and iron ore.
A civil war initially supported by apartheid
South Africa caused widespread loss of life
and damage to infrastructure in the 25 years
following independence from Portugal in
1975. The economy was shattered and large
parts of the country were inaccessible. Human
development suffered and environmental
assessment could not resume until after the
internal peace agreement in 2002. The figures
below should be read in this context, as some
show notable progress in the past decade.
Threats to Angola’s land productivity include
landmines, as well as drought and soil
erosion, which contribute to water pollution
and siltation of rivers and dams. Pressure is
increasing on peri-urban land, in the context
of rural-urban migration and the low incomes
received from urban employment.
Progress towards environmental
sustainability
Reverse the loss of environmental resources
Angola is the most densely forested country
in the Basin (FAO 2010, see Fig. 4.3), including
tropical rainforests in the north. While some
Basin states had deforestation rates as high as
2.2 per cent, Angola shows a rate of between
0.1 and 0.2 per cent, although this is estimated
as many of the forested areas were inaccessible
for a long period. There has been no forestry
inventory in Angola since independence in 1975,
but the Ministry of Agriculture estimates the
minimum reserve at 17.45 million cubic metres of
trees, allowing 20 years of rotational annual cuts.
The use of forestry plantations has been
increasing steadily in Angola, which has the
largest forest plantation area in the Basin,
together with Zimbabwe (SADC and SARDC
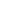
Angola
Z
A
M
B
EZI
R
IV
E
R
B
A
S
I
N
L
I
M
I
T
Mbanza-Congo
Nzeto
Cabinda
Ambriz
LUANDA
Caxito
Songo
Uige
Camabatela
Ndalatando
Dondo
Malanje
Calulo
Quibala
Waku Kungo
Calucinga
Camacupa
Kuito
Huambo
Cubal
Benguela
Lobito
Quipungo
Lubango
Chibia
Chibemba
Namibe
Tombua
Xangongo
Ondjiva
Cuito Cuanavale
Menongue
Muconda
Saurimo
Cacolo
Capenda
Camulemba
Lucapa
Dundo
Lumbala
Nguimbo
Cangamba
Luena
Cazombo
Mavinga
Sumbe
NAMIBIA
ZAMBIA
DEMOCRATIC
REPUBLIC
OF CONGO
ANGOLA
Elevation
Metres above
sea-level
0
200
500
1 000
3 000
2 000
1 500
L
u
n
g
u
e
B
u
n
g
o
C
u
a
n
d
o
C
u
a
n
z
a
K
w
i
l
u
K
w
a
n
g
o
C
u
b
a
n
g
o
C
u
n
e
n
e
C
u
i
t
o