Pelvic nodal dosing and bladder filling?
a relative bladder height change
<
18%
her exact test). Thirty-one kV-CBCTs
xis bony-to-fiducial translation
<
5 mm
and lower than the relative bladder height variations be-
tween groups with acceptable and suboptimal coverage
(
P
<
.001 and
P
<
.05, respectively). Only 2 kV-CBCTs, from
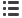
tive planning CTs (left) and kilovoltage cone-beam CTs (right) from 2 patients included in this study.
ical target volume (CTV
N
) 95%; bottom, V
100
CTV
N
65%. Cyan, CTV
N
; magenta, nodal planning target
isodose line; bright red, 95% isodose line; dark red, 90% isodose line. A color version of this figure is
djournal.org .!
2015
Pelvic nodal dosing: Implications fo SBRT
835
03/01/13
Kishan A, IJROBP 2015
Planning
CBCT of the day
Patient 1
Patient 2
Inadequate nodal
coverage if :
?
SI shift on the prostate
>5mm
?
Or variation of bladder
height >18%
3 SOLUTIONS:
1. Enforcing strict
bladder filling
2. Larger nodal PTV
margins
3. Daily online replan or
library of plans