20
AFRICAN FUSION
June 2015
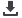
Figure7: Secondary electron SEM images showing morphologies of IN100
after chemical etching; (a): low magnification showing elongated grain
structures; (b): high magnification showing precipitates at grain boundaries
(blocky and elongated shapes) and in the grains (globular shape).
into secondary carbides such as M23C6 and M6C, which tend
to populate the grain boundaries [17].
Crystalline phases and chemical composition
Figure 8 illustrates EDS results of elemental distribution and
shapes and sizes of different types of carbides in the as-
deposited IN100. Similarly, EDS results of post heat-treated
IN100 samples are shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10 by different
etching methods. Although both carbides and borides were
expected to be present as minor phases, borides were not
identified in this work due to low boron concentration and
inherent difficulty in detecting boron by the EDS. Commonly
observed carbides were typically found to contain elements
like molybdenum, chromium, vanadium and titanium. For
instance, refractory elements such as molybdenum are ca-
pable of forming MC carbides, but the bonding with carbon is
weak and hence, MoC can degrade to the more stable forms
of M
23
C
6
and M
6
C after heat treatment or service [17]. MC-type
carbides were seen as globular particles whereas the blocky
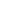
Figure 8: EDS results showing different carbides in the as-deposited IN100.
The globular particles are MC-type whereas the blocky and elongated ones
are M23C6-type. Some of the carbides contain an alumina core.
and elongated ones were M23C6-type. Some of the carbides
contain alumina core that has also been observed by other
researchers [18]. Oxygen may be introduced in the alloy by
interactions with the atmosphere during laser processing.
Trace amounts of oxygen (above 50 ppm) and the subsequent
formation of oxides should be avoided because they cause
grain boundary embrittlement and can significantly reduce
the stress-rupture life of the alloys [20].
Figure 9: EDS results showing different carbides in the post heat-
treated IN100 after electrolytic etching. The globular particles are of
the MC-type whereas the blocky and elongated ones are M23C6-
type. Some of the carbides contain alumina cores.
Figure 10: EDS results showing different carbides in the post heat-
treated IN100 after chemical etching. TiC was observed as black
dots and often found in the grains, while MoC and CrC were seen at
grain boundaries.
Laser aided additive manufacturing