Environment and Security
8
/
The links between
environment
and
security
are the focus
of debate in international policy circles as well as in the
academic community. This report is based on a specific,
conflict-oriented approach to the concept of environmental
security and focuses on identifying linkages between envi-
ronmental degradation and conflict in a given region.
Modern conflicts are complex, unfolding on several levels.
Researchers emphasize that various forms of stress may
engender insecurity whereas other factors promote security
for individuals and groups (see table below).
Although still very broad in its scope, the table below un-
derlines the need to look at the problems and issues that
decrease the resilience of groups and societies and make
them more vulnerable to threats, including the threat of
violent conflict. Empirically it has been difficult to dem-
onstrate that either poverty or environmental factors, in
and by themselves, are strong determinants of conflict.
However, recent research (Ohlsson, 2000) shows that
loss
of livelihoods
is the common denominator for many of the
internal conflicts of the last decades.
Ohlsson argues that “while poverty may be a near-endemic
condition in certain societies, loss of livelihoods marks a
rapid transition from a previous stable condition of relative
welfare into a condition of poverty or destitution”.
It is the
rapid process of change resulting in a sudden fall into pov-
erty that creates the potential for livelihood conflicts
.
There are many possible causes for loss of livelihood in
the contemporary world though they are mostly related to
job scarcity, population growth and environmental deg-
radation of key resources such as water and arable land.
Environmental scarcities
of these two assets constitute
a special case
of growing importance. Although roughly
half the world’s population now lives in cities, agriculture
is still by far the largest single source of livelihoods and
income.
The rapid negative changes associated with the loss of
livelihoods
undermine the resilience of societies
– their
capacity to absorb shocks – and increase vulnerability to
Understanding links between environment and security
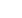
Livelihood Definition
A livelihood comprises the capabilities, assets (stores,
resources, claims, and access) and activities required
for a means of living.
Source: Chambers and Conway, 1992
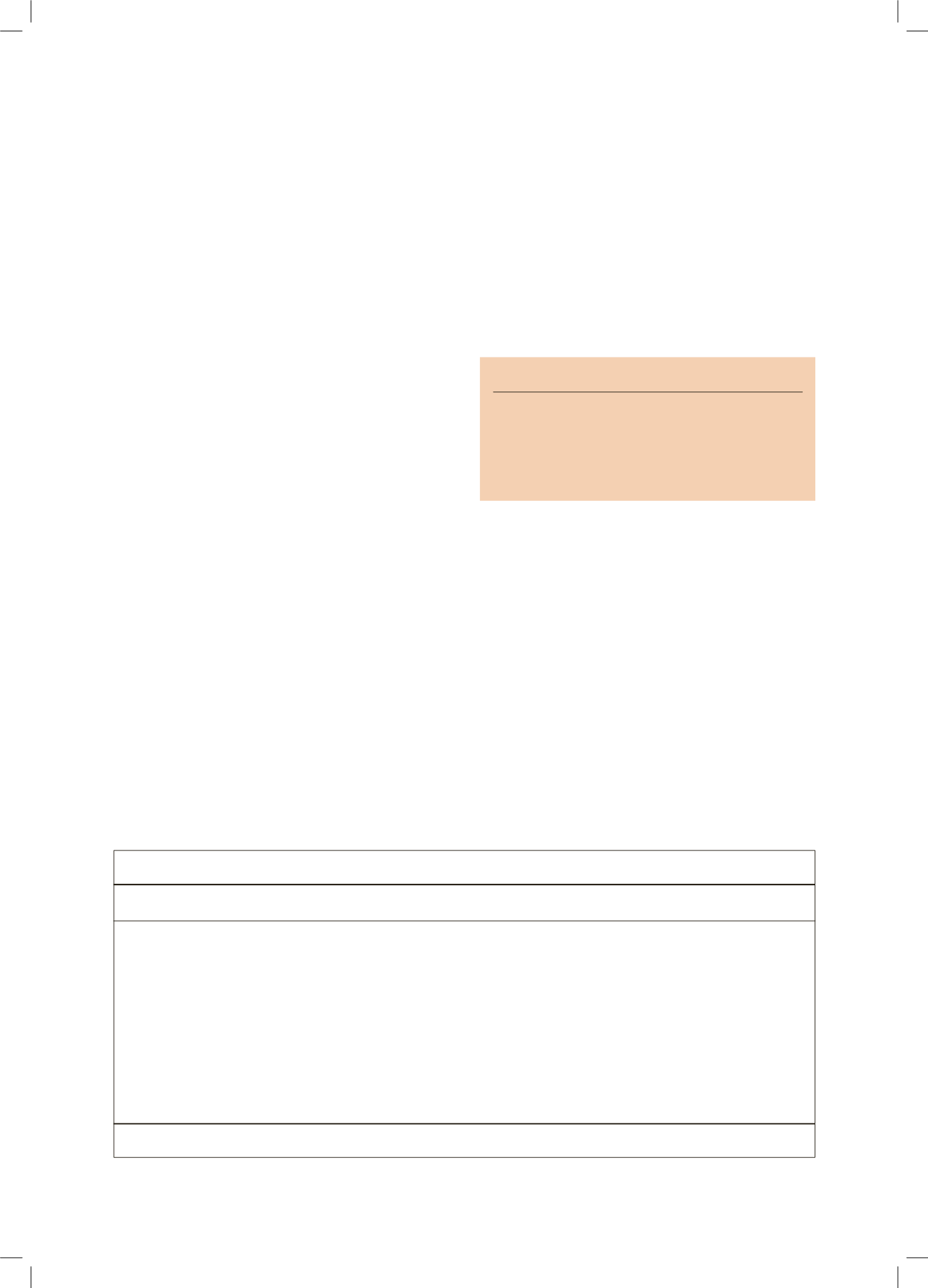
Security-Promoting Mechanisms versus Insecurity-Promoting Mechanisms
System
Economic
Political
Cultural
Demographic
Ecological
Source: Dabelko et al., 2000. in Maltais et al.,2003
Security-Promoting Mechanisms
Wealth
Welfare Policies
Law
Legitimate force
Social identity
Justice
Low birth rate
Urbanization
Life support
Raw materials
Insecurity-Promoting Mechanisms
Poverty
Inequality
Corruption
Unlawful use of force
Discrimination
Injustice
High birth rate
Rapid population flows
Scarcity
Diseases