EuroWire – November 2011
57
technical article
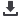
4.2 Hot pressure test
The purpose of this test is to check the
mechanical stability of the cable insulation
and jacket under high thermal and
mechanical load. The test is performed on
the completed cable according to the test
method described in IEC 60811-3-1. Test
temperature is +140°C; the load is applied
for four hours.
4.3 Cold bend test and cold impact test
Solar plants must be able to work under
extreme weather conditions. Thus, the
components are tested not only for high
temperature but also for low temperature
performance. In the German specification
[2]
this is taken into account with high
requirements for the cold bend and cold
impact test. These tests are performed
according to IEC 60811-1-4 at -40°C.
But additionally the cold impact test
is performed with increased height as
well as increased weight of hammer and
intermediate piece.
4.4 Short and long term ageing at
high temperature
A short term ageing test is required at
+150°C with a duration of 168 hours for
the insulation as well as for the jacket
material. Additionally, an Arrhenius test
has to be performed where the materials
have to withstand 20,000 hours at +120°C
(see
Figure 4
).
This enables manufacturers to guarantee
a lifetime of 25 years in the specified
operating conditions.
4.5 Weathering/UV resistance/humidity
To reveal the performance under different
environmental conditions, a weathering
and UV resistance test according to
HD 605/A1, part 2.4.20 is required as
well as a damp heat test according to
EN 60068-2-78.
4.6 Dynamic penetration test
A special penetration test was developed
to prove the stability of the cable jacket
and insulation against mechanical loads.
It is described in Annex E of the discussed
specification
[2]
.
As shown in
Figure 3
, a steel needle is
pressed onto the cable sample. The load
is continuously increased until the needle
contacts the cable conductor, indicated
by a low voltage electrical circuit. The load
in the moment of contact is derived by a
load cell.
This test simulates mechanical loads on
the cable that could be caused by any
object or device falling on the cable or
by animals outside.
4.7 Fire performance
Although the danger of fire propagation in
outdoor applications such as solar plants
is not a great risk for the safety of people,
a good fire performance is required to
protect the technical equipment.
The document
[2]
specifies a flame pro-
pagation test on the completed cable
according to IEC 60332.1.
4.8 Absence of halogens
In the case of fire, acids caused by the
smoke of halogenated materials are
a serious danger for people´s health
as well as for the function of electric
and electronic devices. In former times
halogen free cables were required in
public areas such as hospitals, airports and
other similar structures.
But due to the increasing importance of
electronics in all areas of everyday life, this
quality is increasingly required in industrial
premises, too.
As far as for solar cables, this characteristic
is especially important for solar power
devices on residential buildings.
Several tests have to be performed to
prove the absence of halogens in solar
cables. Electrical conductivity and pH
value of the smoke are to be quantified
▲
▲
Figure 1
:
Pressure test at high temperature on the solar cable
▲
▲
Figure 2
:
Hot elongation test