25
Reduced water availability is expected to play a role in
water quality issues across the region. The countries
are still struggling with pollution problems resulting
from poor sanitation facilities and industrial activities,
including mining pollution. It will affect local aquatic
ecosystems and play a role in water sharing.
Agriculture
While the contribution of agriculture to the
gross domestic product of the three countries has
declined over the past decade, the countries are
still largely dependent on this climate-sensitive
sector. Employment in agriculture and subsistence
farming are vital activities amongst rural mountain
communities where the percentage of poverty is
highest throughout the region. Due to limited arable
land, many families combine crop production with
animal husbandry. In addition, there are other stress
factors such as high levels of land degradation,
including soil erosion and salinization due to a
mix of human activities (e.g. cultivation practices,
overgrazing, and deforestation). Climate change
further exacerbates the situation through increases in
extreme weather events such as heavy precipitation,
which causes soil instability, flooding, and land- and
mudslides (MoENR 2010; MoNP 2015; MoENRP
and UNDP 2015).
The capacity of farmers to adapt to the impacts of climate
change is low due to poorly managed irrigation and
drainage systems, limited financial resources restricting
the use of new technologies, inadequate support from
and access to agricultural extension services, and poor
access to weather and climate information. Thus the
impacts of climate change on agriculture in the South
Caucasus regionmay be severe (Ahouissoussi
et al
. 2014).
Changes in crop yields are one of the most direct ways
climate change is expected to impact agriculture. The
World Bank study “Building Resilience to Climate
Change in South Caucasus Agriculture” (Ahouissoussi
et al
. 2014) includes a comprehensive assessment of the
C
h
o
r
o
k
h
i
H
r
a
z
d
a
n
I
o
r
i
Q
a
b
i
r
l
i
A
g
h
s
t
e
v
K
h
r
a
m
i
Terek
Assa
Argun
D
e
b
e
d
Aras
Samur
Rioni
Rioni
I
n
g
u
r
i
T
s
k
h
e
n
i
s
t
s
k
a
l
i
Vorotan
Voghji
T
e
r
e
k
S
u
l
a
k
Alazani / Ganykh
Aras (Araz)
Arax
A
r
a
s
(
A
r
a
x
)
Kura
Mtkvari (Kura)
K
u
r
(
K
u
r
a
)
Kur
Eastern
Lower
Kura
Basin
Samur-
Middle
Caspian
Basin
Ganykh
Basin
Alazani
Basin
Upper
Aras
Basin
Lankaran-
Vilesh -
Southern
Caspian
Basin
Mingachevir
Reservoir
Lake
Sevan
BLACK SEA
CASPIAN SEA
Lake Van
Sokhumi
Batumi
Nakhchyvan
Baku
Yerevan
Tbilisi
Abkhazia
Nakhchyvan
(Azerbaijan)
Adjara
ARMENIA
GEORGIA
TURKEY
IRAN
AZERBAIJAN
RUSSIAN
FEDERATION
50 km
0
15 14
31
61
13 11
23
35
67 70 77 78
B L M H
B L M H
B L M H
B L M H
95
22
31
21 23
45
55
68 71 75 78
B L M H
B L M H
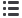
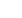
Sources : Ahouissoussi at al., 2014. FAO-AQUASTAT;
www.melioracia.geMap by Manana Kurtubadze, GRID-Arendal, 2015.
Critical river basins border
Irrigated area
23
- Base scenario
- Low Impact scenario
- Medium Impact scenario
- High Impact scenario
B
L
M
H
Percent of irrigation water
demand
Scenarios for 2040
Irrigated zones and water shortage scenarios for 2040 in the South Caucasus