14
AFRICAN FUSION
March 2017
UP peening to prevent fatigue
T
he formation and propagation of cracks in welded
structures plays a critically important role in the total
life cycle of welded components. Ultrasonic Impact
reatment (UIT), also knownUltrasonic Peening (UP), was used
in the rehabilitation and repair of welded elements with the
goal of preventing possible fatigue crack initiation in existing
welded elements and structures that are in service.
A number of large-scalewelded specimens containing no-
load carrying longitudinal attachments designed for fatigue
testing were tested in the as-welded condition and after weld
repair with and without the application of UP.
The testing conditions were zero-to-tension stress cycles
(R=0) with different levels of maximum stresses. The fatigue
testing was stopped and the number of cycles was recorded
when the lengthof fatigue crack on the surface reached 20mm.
Then the fatigue crack was repaired by gouging and welding
and the fatigue test was continued. After repair, the weld toe
of the repair weld was UP treated.
The fatigue testing of all specimens demonstrated that
the repair of fatigue cracks by welding restores the fatigue
strength of welded elements to the initial as-welded condi-
tion. Repairing of fatigue cracks a second and a third time
also practically restored the fatigue life of repaired welded
elements to their initial as-welded condition.
However, when similar samples after the weld repairs
were also treated by UIT/UP, the fatigue life of such samples
was extended by about four times over the samples that were
onlyweld repaired, thus extending the total life cycle of welded
components many times.
Introduction
It is generally accepted that in the total life cycle of welded
components the formation and propagation of cracks in
welded structures plays a pivotal role. Many approaches
exist today for the prevention of crack formation and their
propagation [1, 2].
Thus, for instance, in a comparative study to evaluate the
efficiency of traditional and advanced techniques for fatigue
life improvement of structural elements with fatigue cracks,
a number of large-scale specimens containing fatigue cracks
were repaired using various techniques and subjected to fur-
ther fatigue testing [2]. A number of techniques for restraining
and repairing the fatigue cracks were evaluated and com-
pared, such as: overloading, drilling of the crack tips, drilling
of the crack tips with the installation of high strength bolts,
local explosive treatment, local heat treatment, and welding
with and without UP on the weld toe zones. The fatigue cyclic
testing conditions were zero-to-tension stress cycle (R=0) with
the maximum stresses at 155 MPa.
It was found in this study that the repair of fatigue crack by
welding with the subsequent UP treatment provided the lon-
gest fatigue life in comparison with other ways to prolong the
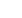
service life of structural elementswith fatigue cracks (Figure 1).
As shown, UP treatment can be effectively applied for fa-
tigue life improvement. It was also demonstrated that UP is a
very efficient treatment during manufacturing, rehabilitation
and repair of welded elements and structures [3-7].
Traditionally, UP treatment is considered inmost cases for
high-cycle fatigue applications, where its effects are mostly
pronounced. It is shown in this paper that in the total life cycle
of welded components, inorder toachieve the longest possible
service time, care must be taken of the welded structures at
all stages of the cycle, that is, through manufacturing, main-
tenance and rehabilitation.
Use of Ultrasonic Peening (UP)
Ultrasonic Peening (UP) is one of the efficientways of achieving
fatigue life improvement of welded elements and structures
[8, 9]. The effects of improvement treatments, particularly UP
treatment, on the fatigue life of welded elements depend on
In this paper, presented at the IIW 2016 Conference in Melbourne, Australia last year,
Jacob Kleiman and Yuri Kudryavtsev of Canada-based Structural Integrity Technologies
(Sintec), present work about the use of ultrasonic impact treatment (UIT), also known as
ultrasonic peening (UP), to prevent fatigue crack initiation and extend the service life of
welded products.
Figure 1: A comparison of the efficiency of different techniques of restraining
and repairing fatigue cracks. 1: Initial condition; 2 and 3: Drilling of the
crack tips with and without cold working; 4: Drilling of the crack tips with
the installation of high strength bolts; 5: Overloading (yield strength); 5′
overloading (0.7 yield strength); 6: Local explosive treatment; 7: Local heat
treatment; 8′: repair by welding with UP treatment of the weld toe zones; and
8′′: Repair by welding without UP.
Extending the life of welded
components
through UP