106
M
ay
2010
www.read-tpt.com›
A
rticle
In this paper the buckling and post-buckling behaviour of stiffened
pipeline is experimentally and theoretically investigated under
hydrostatic pressure. These ring stiffeners were used as buckling
arrestors which cause the buckling capacity to be increased. The
geometric imperfection of specimens is carefully measured and
applied on FEM models but residual stresses are disregarded. The
obtained results are discussed and compared. Also, the effect of
stiffener section as well as the rings spacing are evaluated.
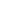
Experimental set-up and procedure
All specimens were manufactured in three small and equal length
parts, and then ring stiffeners added to specimens. All junctions
between these three parts of specimens (circumferential and
longitudinal directions) and specimens-rings junctions were performed
with soldering. Hydrostatic pressure on pipeline was modelled
with a vacuum pump on specimens which absorbing the air in
specimens under loading. Measuring the strains, displacements and
internal pressure of specimens were performed by strain-gauges,
transducers and monometer respectively which were set up on
specimens. For exactly modelling the conditions of specimens on FEM
software, all specimens’ geometric imperfections were measured and
circumferentially and longitudinally meshed (figures 1 and 2).
FEM analysis
All specimens that were tested had both material and geometric
nonlinearity models created. This study was performed by using the
nonlinear finite element program LUSAS. All models were meshed
to 48 parts circumferentially and 96 parts longitudinally (figure 4), by
using 4-noded quadrilateral shell elements (figure 5). The properties
of steel were applied according to the result of steel tension tests that
are shown in figure 3. Material properties and boundary conditions
of models exactly corresponded to experimental conditions.
Figure 3
:
Strain-stress curve of material
Figure 4
:
FEM meshing type
Figure 5
:
Type of using element
Figure 1
:
Strain gauges and transducers set-up
Figure 2
:
Set-up of experiments