UPM Annual Report 2016
UPM Annual Report 2016
22
23
In brief
Businesses
Stakeholders
Governance
Accounts
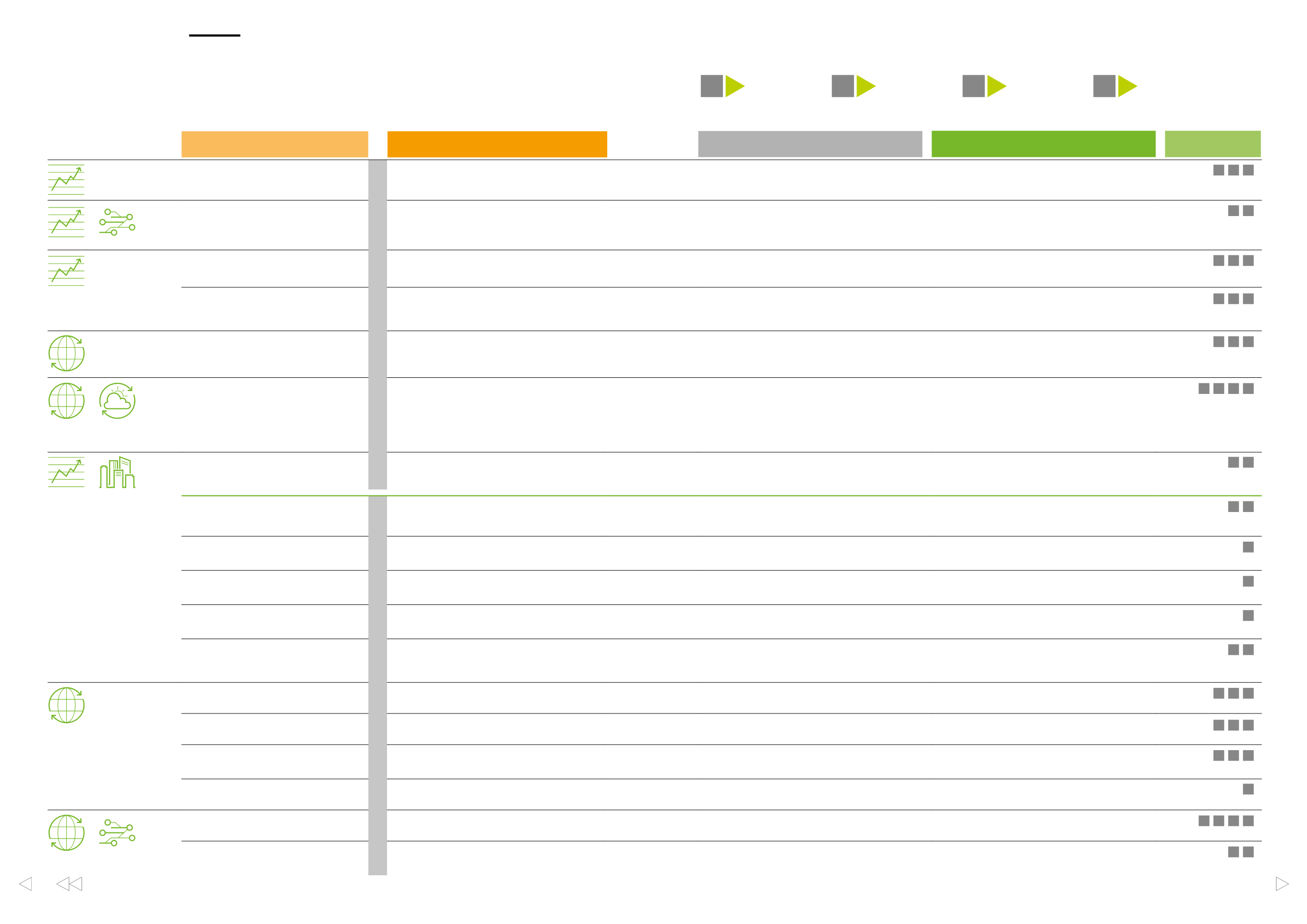
RISK DESCRIPTION
IMPACT
MANAGEMENT
OPPORTUNITY
STRATEGIC FOCUS
AREAS INVOLVED
Global economic cycles
OPERATING ENVIRONMENT
Impacts the demand and sales prices of various UPM products
and main input costs items, as well as currency exchange rates.
UPM’s main earnings sensitivities are presented on page 115.
Industry leading balance sheet. Continuous improvement in
competitiveness, resource efficiency and customer offering.
Business portfolio development.
UPM’s strong balance sheet and focus on competitiveness
mitigate risks and may present strategic opportunities
(incl. M&A) in an economic downturn.
Faster than expected decline in demand
for graphic paper
Increased pressure on UPM’s graphic paper deliveries
and sales prices
Continuous improvement in competitiveness. Focus on more
attractive paper end-use segments. Adjust paper production
capacity to profitable customer demand. Business portfolio
development.
UPM’s large paper production platform provides continuous
optimisation opportunities. Reliable supplier of high quality
products and customer service merits customer loyalty.
Share of UPM businesses in declining markets is decreasing.
Overcapacity in some of UPM’s products
due to changes in demand or supply
Temporarily impacts sales prices and deliveries of the product
in question
Continuous improvement in competitiveness. Disciplined planning
and selection of investments. Business portfolio development.
UPM’s diverse business portfolio, focus on competitiveness and
strong balance sheet mitigate risks and may present strategic
opportunities (incl. M&A) in a cyclical downturn of a business.
Significant moves in currency exchange rates
relevant for UPM
Impacts UPM’s earnings and cash flow directly and
competitiveness indirectly. UPM’s main currency exposures
are presented on page 138.
Continuous hedging of net currency exposure. Hedging the
balance sheet. Continuous improvement in competitiveness.
Disciplined planning and selection of investments. Business
portfolio development.
UPM’s diverse business portfolio and geographical presence,
focus on competitiveness and strong balance sheet mitigate risks
and may present strategic opportunities in changing currency
environment.
International trade barriers,
e.g. antidumping duties
Impacts trade flows and short-term market balances and
may directly or indirectly impact sales prices and deliveries
of UPM’s products.
Monitoring through international trade associations. Continuous
improvement in competitiveness. Disciplined planning and
selection of investments. Business portfolio development.
UPM’s diverse business portfolio and geographical presence
mitigate risks and may present opportunities for optimisation
in case of trade barriers in some products and locations.
Changes in regulation, subsidies, taxation,
e.g. related to climate policies
May distort markets, e.g. for energy or wood raw material.
May change relative competitiveness of energy forms.
May create additional competition for wood raw material.
UPM’s sensitivity to carbon pricing is presented on page 102.
Monitoring for early signals for regulation changes. Communicate
the impacts of such policies on employment and creation of value-
added clearly. Continuous improvement in competitiveness,
materials and energy efficiency. Leading environmental
performance. Innovation and selected investments in value added
renewable products and energy. Business portfolio development.
Sustainable forest management and UPM biodiversity programme.
May drive market growth for sustainable products and energy,
e.g. renewable fuels. Resource efficiency, circular economy and
renewability are increasingly important sources of competitive
advantage. In electricity markets, hydropower is an increasingly
important and competitive form of power generation. Increased
wood growth in northern hemisphere.
Availability and price of major production inputs
like wood, fibre, chemicals and water
Increased cost of raw materials and potential production
interruptions. UPM’s cost structure is presented on page 115
and sensitivity to water prices on page 102.
Continuously improving resource efficiency. Long-term supply
contracts and relying on alternate suppliers. Selected ownership
of forest land and long-term forest management contracts.
UPM’s continuous improvement in resource efficiency and circular
economy mitigate risks and offer competitive advantage.
Continuous improvement in competitiveness
OPERATIONS AND STRATEGY
Weakening relative competitiveness impacts profitability and
increases risks related to the external business environment
(above).
Programmes for savings in variable and fixed costs. Culture
and track record of continuous improvement in productivity
and resource efficiency. Product and service development.
Increasing relative competitiveness improves profitability and
mitigates risks related to the external business environment
(above).
Selection and execution of investment projects
Material cost overruns. Inopportune timing.
Return on investment does not meet targets.
Disciplined selection, planning, project management and
follow-up processes. Investing in projects with attractive returns
and sustainable competitive advantage.
Carefully selected and implemented growth projects improve
UPM’s profitability and ROCE. UPM’s financial targets are
presented on page 17.
OL3 nuclear plant project completion and start-up
Loss of profit and cost overruns. Inopportune timing.
Return on investment does not meet targets.
Ensuring that contractual obligations are met by both parties.
Arbitration proceedings have been initiated by both parties.
The investment provides a competitive, safe and CO
2
emission-free electricity supply for the long term.
Selection and execution of M&A
Cost of acquisition proves high and/or targets for strategic
fit and integration are not met. Return on investment does not
meet targets. Damage to reputation.
Disciplined acquisition preparation to ensure the strategic fit,
right valuation and effective integration. Environmental and social
impact assessments. Stakeholder engagement.
UPM’s strong balance sheet and cash flow enable value-
enhancing M&A when timing and opportunity are right.
Societal value creation.
Developing and commercialising innovations
and new businesses
Return on investment does not meet targets.
Lost opportunity.
Disciplined selection, development and commercialisation of
processes for innovations. Collaboration and partnerships in
R&D and commercialisation. Business model development.
Existing products and services redesigned to bring more value.
New value-added products to replace oil-based materials may
be a significant source of value creation and growth for UPM.
Compliance risks; competition law, anti-corruption,
human rights, securities regulation
Damage to reputation. Loss of business. Fines and damages.
May impact the value of the company.
Governance, compliance procedures, UPM Code of Conduct,
UPM Supplier and Third Party Code, audits, whistleblowing
channel, trainings.
Good governance mitigates risks and promotes best practices.
High responsibility standards and transparency are a
differentiating factor and create long term value.
Supply chain and third party reputation risks
Damage to reputation. Loss of business. Loss of competitive
position. May impact the value of the company.
UPM Code of Conduct, UPM Supplier and Third Party Code,
supplier audits, certification.
Good governance and responsible sourcing practices mitigate
risks and provide competitive advantage.
Environmental risks; a leak or spill due
to malfunction or human error
Damage to reputation. Sanctions. Direct costs to clean up
and repair potential damages to production plant. Loss of
production.
Best available techniques (BAT). Maintenance, internal control
and reports. Certified environmental management systems
(ISO 14001, EMAS).
Industry-leading environmental performance provides competitive
advantage, including efficiency gains.
Physical damage to the employees or property
Harm to employees and damage to reputation.
Damage to assets or loss of production.
One Safety system (p. 45). Loss prevention activities and systems.
Emergency and business continuity procedures.
Leading health and safety performance strengthens the brand
as an employer, as well as improving engagement, efficiency
and productivity.
Ability to retain and recruit skilled personnel
Business planning and execution impaired, affecting long-term
profitability
Competence development. Incentive schemes. Workplace safety.
Acting on employee engagement and management effectiveness.
Engaged high-performing people enable the implementation
of the Biofore strategy, as well as commercial success.
Availability and security of information systems
Interruptions in critical information systems cause a major
interruption to UPM’s business. Damage to reputation.
Loss of business.
Technical, physical and process improvements to mitigate
availability and security risks.
Sophisticated IT systems enable efficient operations, optimised
performance as well as new customer services and data security.
Strategy
Risks and
opportunities
The operating environment exposes UPM to a number of risks and opportunities.
Many of them arise from general economic activity and global megatrends
(see previous page). Execution of strategies exposes UPM and its business areas,
functions and production plants to a number of risks and opportunities.
PERFORMANCE
1
GROWTH
2
PORTFOLIO
3
INNOVATION
4
3 2 1
3 2 1
3 1
3 2 1
3 2 1
4 3 2 1
3 1
2
2
3
4 1
4 1
3 2 1
3 2 1
3 2 1
1
4 3 2 1
4 1
INFLUENCING TRENDS
CONTENTS