
S225
ESTRO 36 2017
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
Conclusion
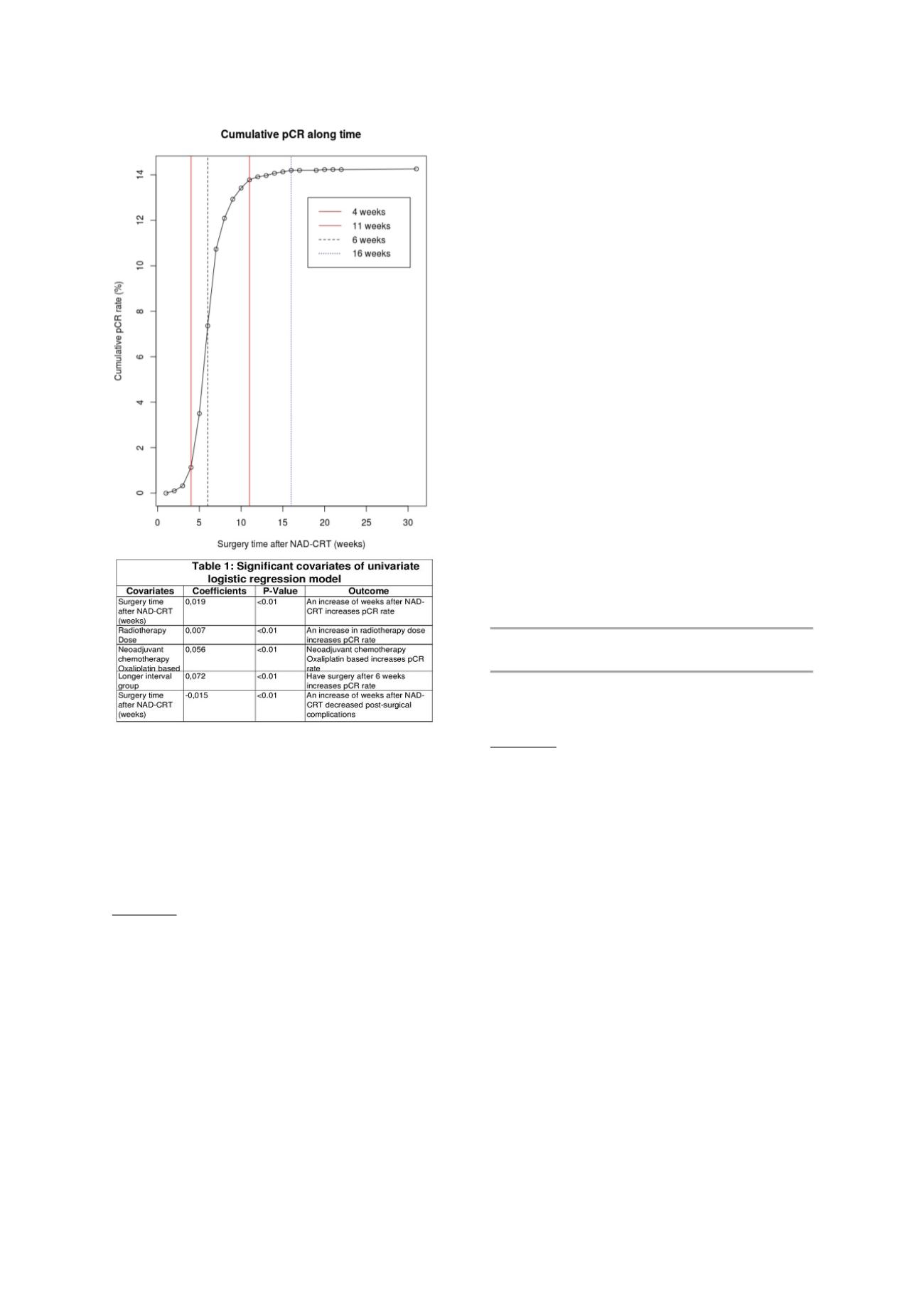
The results of these pooled analyses confirm that the
prolongation of SI after the end of NAD-CRT increased the
rate of pCR in LARC pts. The cumulative pCR rate reached
a plateau at 16 weeks; moreover longer SI has no impact
on post surgical complication rates. No statistically
significant difference was observed in term of survival
outcomes between the SIG and the LIG in pCR pts.
OC-0429 Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy or 5x5 Gy
followed by chemotherapy in rectal cancer: the
RAPIDO trial
C. Marijnen
1
, For the cooperative group of the RAPIDO
trial
2
1
Leiden University Medical Center LUMC, Department of
Radiotherapy, Leiden, The Netherlands
Purpose or Objective
Current standard for the most locally advanced rectal
cancers is preoperative chemoradiotherapy (CRT), and,
variably per institution, postoperative adjuvant
chemotherapy. Short-course preoperative radiation with
delayed surgery induces tumour downstaging in both
randomized and observational studies. In the RAPIDO trial,
the value of short-term preoperative radiotherapy with
5x5 Gy followed by neoadjuvant chemotherapy is
investigated in a randomized fashion.
Material and Methods
Patients with rectal cancer with high risk features for
systemic or local failure on magnetic resonance imaging
were eligible. Randomization took place between a
standard arm A
:
long course chemoradiotherapy followed
by TME surgery and optional postoperative
chemotherapy and an experimental arm B:
short course 5
x 5 Gy radiation followed by six cycles of full-dose CAPOX
or nine cycles of FOLFOX and TME surgery.
Results
A total of 920 patients were included between June 2011
and June 2016. At randomisation, 302 were cT4 and 828
were cN+, of whom 621 were considered cN2 disease and
137 as extramesorectal pelvic lymphnodes. Based on MRI,
extramural vascular invasion was diagnosed in 275
patients, whereas the mesorectal fascia was threatened in
564 patients.
Preliminary data show that median time between
randomization and surgery was 15,9 weeks for arm A and
25,3 weeks for arm B. In arm B, 100% of the patients who
started, completed the radiotherapy and 72% of patients
completed all scheduled cycles of neoadjuvant
chemotherapy after 5x5 Gy. Another 9% of patients
completed the last course(s) without oxaliplatin. In arm A,
96% received all scheduled radiotherapy fractions and 94%
of the patients received 5 weeks of preoperative
capecitabine
combined
with
radiotherapy.
Open surgery was performed in 59% of the patients and
35% underwent an APR. In total, 19% of patients had a
ypT0N0. For 4% of all patients a wait & watch strategy was
applied. Of the operated patients, 89% had a negative
circumferential resection margin (> 1 mm).
Conclusion
Compliance for neoadjuvant treatment was good in both
treatment arms. Given the locally advanced state of most
tumors, the ypT0N0 rate can be considered satisfactory.
Final data and details concerning differences in pre-
treatment characteristics and treatments between the
two arms will be presented.
Joint Symposium: ESTRO-ESR: Radiomics and imaging
databases for precision radiation oncology
SP-0430 Radiomics in radiology, what are the
parameters of interest for different imaging
modalities?
H. Ahlström
1
1
Uppsala University, Dept of Radiology, Uppsala, Sweden
CT, MRI, PET, PET-CT and PET-MRI datasets contain huge
amounts of spatially detailed morphological, functional
and metabolic information. Today, when analysed, these
detailed datasets are typically heavily reduced to a few
measurements of a priori specified measurements of
interest
(e.g.
volumes,
areas,
diameters,
average/maximum tracer concentrations etc.) and/or
visually – and therefore inevitably subjectively – assessed
by a human operator. As a result, normality/non-normality
can only be assessed on these measurements and not on
the entire data collected, and statistical interaction with
non-imaging parameters can also be assessed only on
these a priori specified measurements. In order to utilise
the full potential of these image datasets, new analysis
tools included in the concept Radiomics, that allow
objective or quantitative assessment of all imaging data
(including e.g. previously discarded information about
texture), are needed. Radiomics can be divided into
distinct processes: (a) image acquisition and
reconstruction, (b) image segmentation and rendering, (c)
feature extraction and feature qualification and (d)
databases and data sharing with non-imaging data (e.g.
different “omics” and clinical data) for (e) informatics
analyses. Statistical knowledge of the normal range of
Radiomics features are needed for the analyses. These
analyses are anticipated to bring out new associations and
understandings that traditional approaches could not
achieve. Radiomics features can, together with non-
imaging data, be included in models that have shown to


















