62 |
Ten Year Network Development Plan 2015
0
400
200
600
800
1,200
1,000
Filling
stations
0
900,000
800,000
700,000
600,000
500,000
400,000
300,000
200,000
100,000
Vehicles
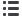
AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GR HR HU IE IT LT LU LV MT NL PL PT RO SE SI SK UK
Filling stations
Number of natural gas vehicles 2013
Figure 4.30:
Natural gas vehicles (2013) and CNG filling stations (2014), country detail (Source Eurogas/NGVA Europe)
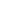
n.a.
1 – 50
50 – 200
200 – 500
500 – 2,000
Ratio vehicles/filling stations
Figure 4.31:
Ratio of vehicles per CNG filling station, ENTSOG depiction (Source Eurogas/NGVA Europe)
4.3.4 GAS DEMAND FOR TRANSPORTATION
Besides being used in the residential, commercial and industrial sectors as well as
for power generation, gas is becoming more favored as a fuel for transportation
purposes. In order to have a wider range of potential future gas demand scenarios,
TSOs have been asked to provide gas projections for the maritime and road trans-
portation sectors based on the same assumption as used for the Green and Grey
scenarios .
Compressed natural gas (CNG) for road transportation (mainly light duty vehicles –
LDV) is currently the most mature market in Europe with close to 1 million vehicles
adapted to this technology and around 3,000 fillings stations. The highest numbers
of filling stations are found in Italy, Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Netherlands,
Finland and Bulgaria.
LNG has cleaner exhaust emissions and higher energy efficiency. LNG could be used
as a replacement for heavy oil fuel in sea-born transportation and for diesel in inland-
water transportation. On-shore LNG bunker facilities
1)
for vessels are already in place
1) Bunker facilities are referring to LNG refilling station for ships.