39
The main risks associated with climate change are
related to the economy, human safety and security,
and changes in ecosystem services. Considering
Key risks related to climate change
their relevance to concrete adaptation measures, the
risks are clustered below according to key economic
activities and ecosystems. The identified risks result
from interaction between possible hazards fully or
partly triggered by climate change and vulnerabilities
of existing human systems.
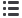
Key vulnerabilities
• Predicted upward shift of climatic zones and vegetation.
Loss of control of pests and disease, fires, landslides,
flooding, erosions etc. Reduction in provision of services
(e.g. food, livestock).
• Vulnerability of agriculture sector, vulnerability of selected
social groups including rural remote communities.
• High degree of land degradation and desertification, soil
erosion etc.
• Poor land management. Poor water management in and
between economic sectors.
• Limited ability of framers to adapt and administrative
systems to respond. Poor compensation mechanisms in
cases of breakdowns.
Key risks
8
• Reduction of ecosystem services (water purification,
preservation of soil).
• Loss or change of ecosystems (e.g. water ecosystem, forest
ecosystems). Loss of endemic species, mixing ecosystem types,
increase numbers of invasive spices.
• Increase in wildfires
• Decrease in productivity and decrease in crop yields (and
livestock) leading to outbreaks in food availability and
security of seeds.
• Risk of resource loss e.g. agro-biodiversity and land.
• Lost agriculture and pastureland or reduction in its
productivity.
• Damage of infrastructure.
• Increase in conflicts between the water-based sectors such as
energy and agriculture.
Summary of Key hazards, vulnerabilities and risks
➔
Climate hazards
Ecosystems
• Increase in temperature, changes in
precipitation. Droughts. Intensity
and frequency of extreme heat.
• Increase in number of natural
disasters land slides, mudslides etc.
Agriculture
• Increase in temperature, changes
in precipitation pattern.
• Extreme weather events such as
hail storms, late frosts, strong
winds, heavy rainfalls, droughts
etc.