ACCOUNTS
UPM Annual Report 2016
UPM Annual Report 2016
140
141
In brief
Strategy
Businesses
Stakeholders
Governance
Accounts
CONTENTS
Hedges of net investments in foreign subsidiaries
The fair value changes of forward exchange contracts used in hedging
net investments that reflect the change in spot exchange rates are
recognised in other comprehensive income within translation reserve.
Any gain or loss relating to the interest portion of forward exchange
contracts is recognised immediately in the income statement under
financial items. Gains and losses accumulated in equity are included
in the income statement when the foreign operation is partially disposed
of or sold.
Fair value hedges
The group applies fair value hedge accounting for hedging fixed interest
risk on debt. Changes in the fair value of derivatives that are designated
and qualify as fair value hedges and that are highly effective both
prospectively and retrospectively are recorded in the income statement
under financial items, along with any changes in the fair value of the
hedged asset or liabilities that are attributable to the hedged risk.
The carrying amounts of hedged items and the fair values of hedging
instruments are included in interest-bearing assets or liabilities.
Derivatives that are designated and qualify as fair value hedges mature
at the same time as hedged items. If the hedge no longer meets the
criteria for hedge accounting, the adjustment to the carrying amount
of a hedged item for which the effective interest method is used is
amortised to profit or loss over the expected period to maturity.
Financial counterparty risk
The financial instruments the group has agreed with banks and financial
institutions contain an element of risk of the counterparties being
unability to meet their obligations. According to the Group Treasury
Policy derivative instruments and investments of cash funds may be
made only with counterparties meeting certain creditworthiness criteria.
The group minimises counterparty risk also by using a number of major
banks and financial institutions. Creditworthiness of counterparties is
constantly monitored by Treasury and Risk Management.
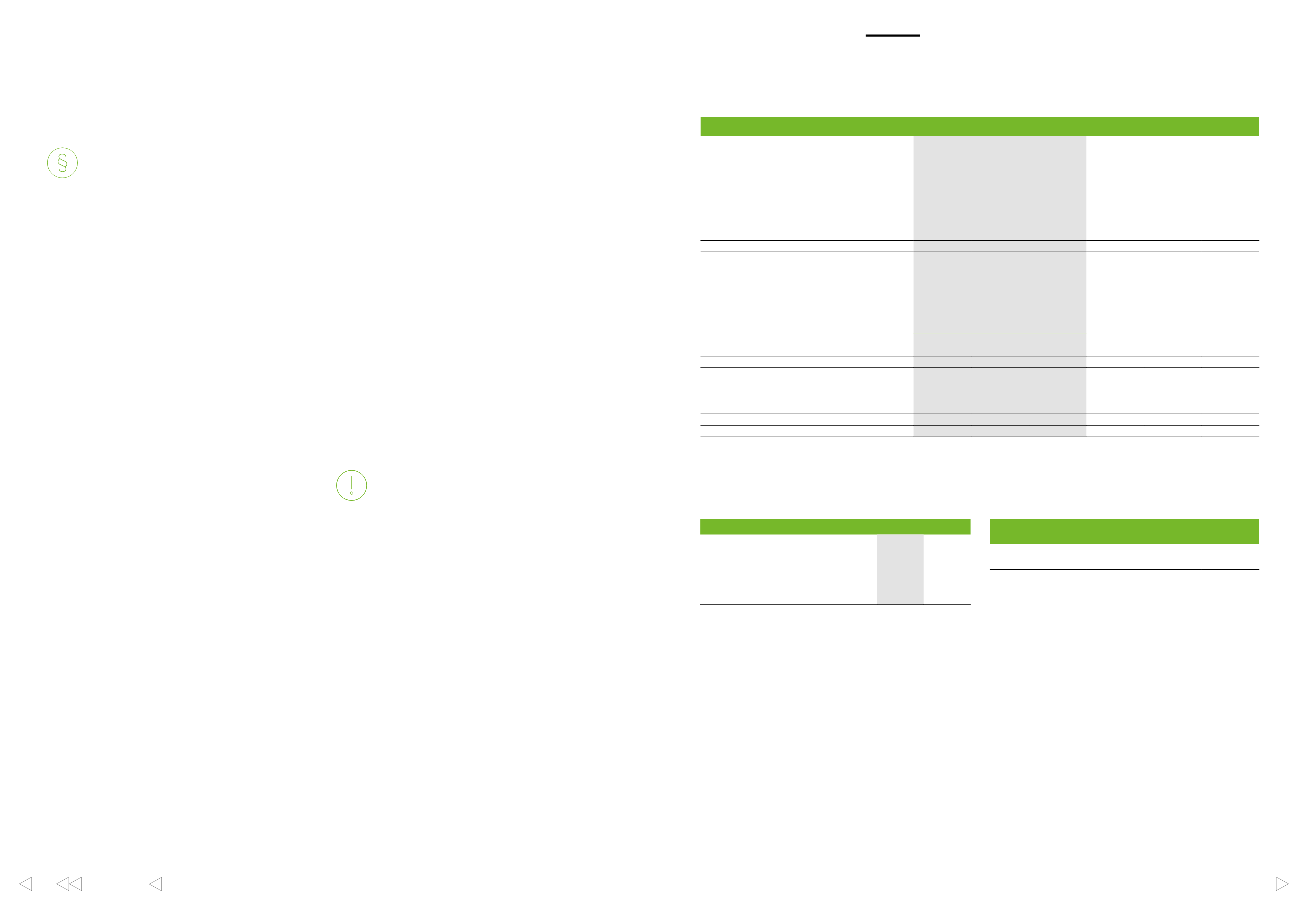
No derivatives are subject to offsetting in the group’s financial statements. All derivatives are under ISDA or similar master netting agreement.
Positive
fair values
Negative
fair values
Net
fair values
Positive
fair values
Negative
fair values
Net
fair values
EURm
2016
2015
Foreign exchange risk
Forward foreign exchange contracts
Cash flow hedges
35
–41
–6
17
–27
–10
Net investment hedge
4
–19
–15
–
–21
–21
Non-qualifying hedges
10
–14
–4
14
–14
–
Currency options
Non-qualifying hedges
–
–
–
–
–
–
Cross currency swaps
Non-qualifying hedges
23
–77
–54
15
–46
–31
Derivatives hedging foreign exchange risk
72
–151
–79
46
–108
–62
Interest rate risk
Interest rate swaps
Cash flow hedges
–
–34
–34
–
–18
–18
Fair value hedges
138
–
138
181
–
181
Non-qualifying hedges
27
–2
25
31
–2
29
Cross currency swaps
Cash flow hedges
–
–
–
–
–23
–23
Fair value hedges
64
–
64
85
–
85
Non-qualifying hedges
1
–
1
1
–
1
Derivatives hedging interest risk
230
–36
194
298
–43
255
Commodity risk
Commodity contracts
Cash flow hedges
32
–42
–10
88
–109
–21
Non-qualifying hedges
5
–19
–14
8
–59
–51
Derivatives hedging commodity risk
37
–61
–24
96
–168
–72
Total
339
–248
91
440
–319
121
EURm
POSITIVE
FAIR VALUES
NEGATIVE
FAIR VALUES
NET
FAIR VALUES
2016
238
–148
90
2015
250
–129
121
6.2 Derivatives and hedge accounting
The group uses financial derivatives to manage currency, interest rate
and commodity price risks.
» Refer Note 6.1
Financial risk
management.
Accounting policies
All derivatives are initially and continuously recognised at fair value in
the balance sheet. The fair value gain or loss is recognised through the
income statement or other comprehensive income depending on whether
the derivative is designated as a hedging instrument, and on the nature
of the item being hedged. Certain derivatives are designated at inception
either hedges of the fair value of a recognised assets or liabilities or
a firm commitment (fair value hedge), hedges of highly probable
forecasted transactions or cash flow variability in functional currency
(cash flow hedge), or hedges of net investments in foreign subsidiaries
with other than the EUR as their functional currency (net investment
hedge). Derivative fair values on the balance sheet are classified as
non-current when the remaining maturity is more than 12 months and
as current when the remaining maturity is less than 12 months.
For hedge accounting purposes, UPM documents the relationship
between the hedging instruments and hedged items, as well as the
risk management objective and strategy for undertaking various
hedge transactions at the inception date. This process includes linking
all derivatives designated as hedges to specific assets and liabilities
or to specific firm commitments or forecast transactions. The group
also documents its assessment, both at the hedge inception and on
an on-going basis, as to whether the hedge is highly effective in
offsetting changes in fair values or cash flows of the hedged items.
Certain derivatives, while considered to be economical hedges for
UPM’s financial risk management purposes, do not qualify for hedge
accounting. Such derivatives are recognised at fair value through the
income statement in other operating income or under financial items.
Cash flow hedges
The effective portion of changes in the fair value of derivatives that
are designated and qualify as cash flow hedges is recognised in other
comprehensive income. Amounts deferred in equity are transferred to
the income statement and classified as income or expense in the same
period as that in which the hedged item affects the income statement
(for example, when the forecast external sale to the group that is hedged
takes place). The period when the hedging reserve is released to sales
after each derivative has matured is approximately one month. The gain
or loss relating to the effective portion of interest rate swaps hedging
variable rate borrowings is recognised in the income statement within
finance costs. When the forecasted transaction that is hedged results
in the recognition of a fixed asset, gains and losses previously deferred
in equity are transferred from equity and included in the initial
measurement of the acquisition cost and depreciated over the useful lives
of the assets.
When a hedging instrument expires or is sold, or when a hedge
no longer meets hedge accounting criteria, any cumulative gain or
loss existing in equity at that time remains in equity and is recognised
when the committed or forecasted transaction is ultimately recognised
in the income statement. However, if a forecasted transaction is no
longer expected to occur, the cumulative gain or loss that was
reported in equity is immediately recognised to the income statement.
EURm
2016
2015
Interest rate forward contracts
1,480
1,906
Interest rate swaps
2,019
2,131
Forward foreign exchange contracts
2,645
2,949
Currency options
36
73
Cross currency swaps
557
669
Commodity contracts
429
400
Cash collaterals pledged for derivative contracts totalled EUR
19 million of which EUR 17 million relate to commodity contracts
and EUR 2 million to interest rate forward contracts.
Net fair values of derivatives
Net fair values of derivatives calculated by counterparty
Notional amounts of derivatives